Lactobacillus rhamnosus attenuates bone loss and maintains bone health by skewing Treg-Th17 cell balance in Ovx mice
- PMID: 33469043
- PMCID: PMC7815799
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-80536-2
Lactobacillus rhamnosus attenuates bone loss and maintains bone health by skewing Treg-Th17 cell balance in Ovx mice
Abstract
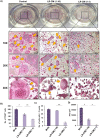
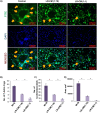
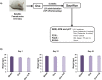
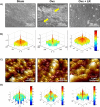
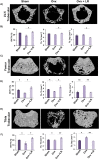
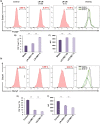
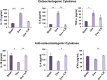
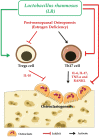
Osteoporosis is a systemic-skeletal disorder characterized by enhanced fragility of bones leading to increased rates of fractures and morbidity in large number of populations. Probiotics are known to be involved in management of various-inflammatory diseases including osteoporosis. But no study till date had delineated the immunomodulatory potential of Lactobacillus rhamnosus (LR) in bone-health. In the present study, we examined the effect of probiotic-LR on bone-health in ovariectomy (Ovx) induced postmenopausal mice model. In the present study, we for the first time report that LR inhibits osteoclastogenesis and modulates differentiation of Treg-Th17 cells under in vitro conditions. We further observed that LR attenuates bone loss under in vivo conditions in Ovx mice. Both the cortical and trabecular bone-content of Ovx+LR treated group was significantly higher than Ovx-group. Remarkably, the percentage of osteoclastogenic CD4+Rorγt+Th17 cells at distinct immunological sites such as BM, spleen, LN and PP were significantly reduced, whereas the percentage of anti-osteoclastogenic CD4+Foxp3+Tregs and CD8+Foxp3+Tregs were significantly enhanced in LR-treated group thereby resulting in inhibition of bone loss. The osteoprotective role of LR was further supported by serum cytokine data with a significant reduction in osteoclastogenic cytokines (IL-6, IL-17 and TNF-α) along with enhancement in anti-osteoclastogenic cytokines (IL-4, IL-10, IFN-γ) in LR treated-group. Altogether, the present study for the first time establishes the osteoprotective role of LR on bone health, thus highlighting the immunomodulatory potential of LR in the treatment and management of various bone related diseases including osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bacillus clausii inhibits bone loss by skewing Treg-Th17 cell equilibrium in postmenopausal osteoporotic mice model.Nutrition. 2018 Oct;54:118-128. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.02.013. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Nutrition. 2018. PMID: 29793054
-
Bifidobacterium longum Ameliorates Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss via Enhancing Anti-Osteoclastogenic and Immunomodulatory Potential of Regulatory B Cells (Bregs).Front Immunol. 2022 May 25;13:875788. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.875788. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35693779 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-osteoporotic potential of a probiotic mixture containing Limosilactobacillus reuteri and Weissella cibaria in ovariectomized rats.Sci Rep. 2025 May 27;15(1):18586. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02089-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40425630 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure.Gut Microbes. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2190304. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2190304. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 36941563 Free PMC article.
-
Immune regulation of bone loss by Th17 cells in oestrogen-deficient osteoporosis.Eur J Clin Invest. 2013 Nov;43(11):1195-202. doi: 10.1111/eci.12158. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Eur J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 24033116 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term implications of COVID-19 on bone health: pathophysiology and therapeutics.Inflamm Res. 2022 Sep;71(9):1025-1040. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01616-9. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35900380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of targeted therapy regulating Th17/Treg balance in bone immune diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 30;15:1333993. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1333993. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38352872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the osteoclastogenic cytokine IL-9 as a novel immunotherapeutic strategy in mitigating inflammatory bone loss in post-menopausal osteoporosis.JBMR Plus. 2024 Sep 14;8(11):ziae120. doi: 10.1093/jbmrpl/ziae120. eCollection 2024 Nov. JBMR Plus. 2024. PMID: 39399159 Free PMC article.
-
Gut-bone axis perturbation: Mechanisms and interventions via gut microbiota as a primary driver of osteoporosis.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Jan 21;50:373-387. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.11.003. eCollection 2025 Jan. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 40171106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biotechnological Processes Simulating the Natural Fermentation Process of Bee Bread and Therapeutic Properties-An Overview.Front Nutr. 2022 Apr 27;9:871896. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.871896. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35571893 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

