Detection of QTNs for kernel moisture concentration and kernel dehydration rate before physiological maturity in maize using multi-locus GWAS
- PMID: 33469070
- PMCID: PMC7815807
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-80391-1
Detection of QTNs for kernel moisture concentration and kernel dehydration rate before physiological maturity in maize using multi-locus GWAS
Abstract
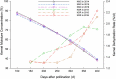
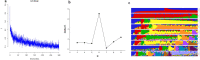
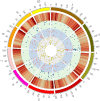
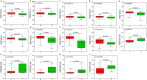
Maize is China's largest grain crop. Mechanical grain harvesting is the key technology in maize production, and the kernel moisture concentration (KMC) is the main controlling factor in mechanical maize harvesting in China. The kernel dehydration rate (KDR) is closely related to the KMC. Thus, it is important to conduct genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of the KMC and KDR in maize, detect relevant quantitative trait nucleotides (QTNs), and mine relevant candidate genes. Here, 132 maize inbred lines were used to measure the KMC every 5 days from 10 to 40 days after pollination (DAP) in order to calculate the KDR. These lines were genotyped using a maize 55K single-nucleotide polymorphism array. QTNs for the KMC and KDR were detected based on five methods (mrMLM, FASTmrMLM, FASTmrEMMA, pLARmEB, and ISIS EM-BLASSO) in the package mrMLM. A total of 334 significant QTNs were found for both the KMC and KDR, including 175 QTNs unique to the KMC and 178 QTNs unique to the KDR; 116 and 58 QTNs were detected among the 334 QTNs by two and more than two methods, respectively; and 9 and 5 QTNs among 58 QTNs were detected in 2 and 3 years, respectively. A significant enrichment in cellular component was revealed by Gene Ontology enrichment analysis of candidate genes in the intervals adjacent to the 14 QTNs and this category contained five genes. The information provided in this study may be useful for further mining of genes associated with the KMC and KDR in maize.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multi-Locus Genome-Wide Association Study and Genomic Selection of Kernel Moisture Content at the Harvest Stage in Maize.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jul 9;12:697688. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.697688. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34305987 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of multi-locus genome-wide association study and QTL mapping reveals genetic basis of tassel architecture in maize.Mol Genet Genomics. 2019 Dec;294(6):1421-1440. doi: 10.1007/s00438-019-01586-4. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Mol Genet Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31289944
-
The Application of Multi-Locus GWAS for the Detection of Salt-Tolerance Loci in Rice.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Oct 4;9:1464. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01464. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30337936 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association studies and whole-genome prediction reveal the genetic architecture of KRN in maize.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Oct 27;20(1):490. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02676-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 33109077 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Dissection of Maize Embryonic Callus Regenerative Capacity Using Multi-Locus Genome-Wide Association Studies.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Apr 26;9:561. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00561. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29755499 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
QTL mapping and omics analysis to identify genes controlling kernel dehydration in maize.Theor Appl Genet. 2024 Sep 26;137(10):233. doi: 10.1007/s00122-024-04715-9. Theor Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 39325221
-
Utilizing Two Populations Derived from Tropical Maize for Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Banded Leaf and Sheath Blight Resistance.Plants (Basel). 2024 Feb 4;13(3):456. doi: 10.3390/plants13030456. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337988 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals the Genetic Basis of Kernel and Cob Moisture Changes in Maize at Physiological Maturity Stage.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jul 30;11(15):1989. doi: 10.3390/plants11151989. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35956467 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic dissection of maize grain moisture content and dehydration rate using high-density bin mapping in a recombinant inbred line population.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Mar 21;25(1):369. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06404-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40119273 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Density Reference Fingerprinting SNP Dataset of CIMMYT Maize Lines for Quality Control and Genetic Diversity Analyses.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 14;11(22):3092. doi: 10.3390/plants11223092. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China . China Statistical Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistical Press; 2019. pp. 1–12.
-
- Chai ZH, et al. Current status of maize mechanical grain harvesting and its relationship with grain moisture content. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2017;50:2036–2043. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.11.009. - DOI
-
- Xiang K, Reid LM, Zhang ZM, Zhu XY, Pan GT. Characterization of correlation between grain moisture and ear rot resistance in maize by QTL meta-analysis. Euphytica. 2012;183:185–195. doi: 10.1007/s10681-011-0440-z. - DOI
-
- Sweeney PM, St Martin SK, Clucas CP. Indirect inbred selection to reduce grain moisture in maize hybrids. Crop Sci. 1994;34:391–396. doi: 10.2135/cropsci1994.0011183X003400020016x. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

