Decreased serum betatrophin may correlate with the improvement of obstructive sleep apnea after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass surgery
- PMID: 33469084
- PMCID: PMC7815868
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-81379-1
Decreased serum betatrophin may correlate with the improvement of obstructive sleep apnea after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass surgery
Abstract
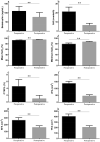
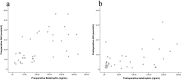
Obesity is strongly correlated with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and bariatric surgery can effectively treat obesity and alleviate OSA. However, the contributing factors are still unclear. We aimed to explore the relationship between betatrophin and OSA in patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery. Our study consisted of thirty-seven individuals with OSA and type 2 diabetes (16 males, 21 females) undergoing RYGB surgery. The polysomnography test, anthropometric results, serum betatrophin, and abdominal magnetic resonance images were evaluated both before and 1 year after RYGB surgery. Factors that may correlate with the alleviation of OSA were investigated. In our study, RYGB surgery significantly decreased apnea hypopnea index (AHI) and serum betatrophin concentration (p < 0.001). The abdominal visceral fat area, subcutaneous fat area and HOMA-IR were also significantly decreased (p < 0.001). The preoperative AHI, postoperative AHI and the change in AHI were significantly correlated with the preoperative betatrophin, postoperative betatrophin and the change in betatrophin, respectively (p < 0.05). These correlations were still significant after adjustment for other risk factors. The change in betatrophin was also independently associated with the change in minimum oxygen saturation (p < 0.001). Our data might indicate that serum betatrophin was significantly independently correlated with the improvement of OSA after bariatric surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

