Maternal endothelial dysfunction in HIV-associated preeclampsia comorbid with COVID-19: a review
- PMID: 33469197
- PMCID: PMC7815501
- DOI: 10.1038/s41440-020-00604-y
Maternal endothelial dysfunction in HIV-associated preeclampsia comorbid with COVID-19: a review
Abstract
This review assesses markers of endothelial dysfunction (ED) associated with the maternal syndrome of preeclampsia (PE). We evaluate the role of antiretroviral therapy (ART) in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected preeclamptic women. Furthermore, we briefly discuss the potential of lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r), dolutegravir (DTG) and remdesivir (RDV) in drug repurposing and their safety in pregnancy complicated by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. In HIV infection, the trans-activator of transcription protein, which has homology with vascular endothelial growth factor, impairs angiogenesis, leading to endothelial injury and possible PE development despite neutralization of their opposing immune states. Markers of ED show strong evidence supporting the adverse role of ART in PE development and mortality compared to treatment-naïve pregnancies. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection, exploits angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE 2) to induce ED and hypertension, thereby mimicking angiotensin II-mediated PE in severe cases of infection. Upregulated ACE 2 in pregnancy is a possible risk factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent PE development. The potential effectiveness of LPV/r against COVID-19 is inconclusive; however, defective decidualization, along with elevated markers of ED, was observed. Therefore, the safety of these drugs in HIV-positive pregnancies complicated by COVID-19 requires attention. Despite the observed endothelial protective properties of DTG, there is a lack of evidence of its effects on pregnancy and COVID-19 therapeutics. Understanding RDV-ART interactions and the inclusion of pregnant women in antiviral drug repurposing trials is essential. This review provides a platform for further research on PE in the HIV-COVID-19 syndemic.
Keywords: Antiretrovirals; Endothelial dysfunction; HIV; Preeclampsia; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
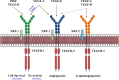


References
-
- World Health Organization. Maternal mortality. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/maternal-mortality. Accessed 21 February 2020.
-
- Brown MA, Magee LA, Kenny LC, Karumanchi SA, McCarthy FP, Saito S, et al. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: ISSHP Classification, Diagnosis, and Management Recommendations for International Practice. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex: 1979) 2018;72:24–43. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10803. - DOI - PubMed
-
- National Committee for Confidential Enquiry into Maternal Deaths. Saving Mothers Report 2017. Pretoria: South African Department of Health; 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

