miR-21 Induces Chemoresistance in Ovarian Cancer Cells via Mediating the Expression and Interaction of CD44v6 and P-gp
- PMID: 33469309
- PMCID: PMC7811474
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S286639
miR-21 Induces Chemoresistance in Ovarian Cancer Cells via Mediating the Expression and Interaction of CD44v6 and P-gp
Abstract
Background: Ovarian cancer (OC), a representative female reproductive system tumor, is one of the most malignant tumors in female. The most important reason for its poor prognosis is because of its high rate of chemotherapy resistance.
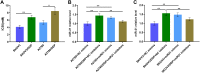
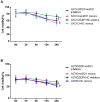
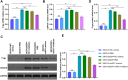
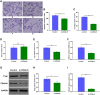
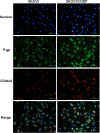
Results: This study aims to explore the effects of miR-21 on the chemotherapy resistance of OC cells. The functions of miR-21 on proliferation, migration and invasion of OC cells were assessed by transwell, clonal formation and CCK8 assay. Expression levels of miR-21, P-gp and CD44v6 in SKOV3 (cisplatin sensitive) cells and SKOV3/DDP (cisplatin resistant) cells were detected by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blotting. Si-CD44v6 was transfected into OC cells to detect the influence on P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expression. Immunofluorescence was used to detect the localization of CD44v6 and P-gp in cell. Co-immunoprecipitation was used to detect the relationship between CD44v6 and P-gp. Results showed that miR-21 expression in cisplatin-resistant SKOV3/DDP cells was significantly higher than that in SKOV3 cells, at the same time, cells proliferation, as well as invasion and migration ability were enhanced after the miR-21 mimics transfected into SKOV3 cisplatin-sensitive cells. Furthermore, miR-21 expression level affected the CD44v6 and P-gp expression. Immunofluorescence and co-immunoprecipitation showed that CD44v6 and P-gp protein could interact.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the high miR-21 expression level could increase the proliferation, invasion, and migration ability of OC cells. And the interaction of CD44v6 and P-gp may mediate miR-21 involvement in chemotherapy resistance of OC cells.
Keywords: CD44v6; P-glycoprotein; chemotherapy resistance; ovarian cancer.
© 2021 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-132 reverses cisplatin resistance and metastasis in ovarian cancer by the targeted regulation on Bmi-1.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 May;23(9):3635-3644. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201905_17787. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31114988
-
Exosomal miR-21-5p derived from cisplatin-resistant SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells promotes glycolysis and inhibits chemosensitivity of its progenitor SKOV3 cells by targeting PDHA1.Cell Biol Int. 2021 Oct;45(10):2140-2149. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11671. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Cell Biol Int. 2021. PMID: 34288231
-
CD44v6 may influence ovarian cancer cell invasion and migration by regulating the NF-κB pathway.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jul;18(1):298-306. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10306. Epub 2019 May 3. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31289500 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of miR-1246 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Cisplatin-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cells by Promoting ZNF23 Transcription.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2021;161(10-11):488-500. doi: 10.1159/000520069. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2021. PMID: 34923485
-
[Expression of microRNA-100 and its correlation with drug resistance in human ovarian cancer SKOV3/DDP cells].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015 Nov;35(11):1624-7. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26607088 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Role of MicroRNA-21 in Prostate Cancer Progression and Metastasis: Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Targets.Ann Surg Oncol. 2024 Jul;31(7):4795-4808. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-15453-z. Epub 2024 May 17. Ann Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38758485 Review.
-
Ultrasensitive Impedimetric Biosensor for Ovarian Cancer Screening.Indian J Microbiol. 2025 Mar;65(1):439-452. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01307-5. Epub 2024 May 23. Indian J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40371031
-
Activatable "Matryoshka" nanosystem delivery NgBR siRNA and control drug release for stepwise therapy and evaluate drug resistance cancer.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Mar 19;14:100245. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100245. eCollection 2022 Mar. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35345559 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of the JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway in drug resistance in ovarian cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 24;15:1533352. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1533352. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40352594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Heavy Metals in the Biology of Female Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 28;26(11):5155. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115155. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507964 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

