Nasal Obstruction as a Potential Factor Contributing to Hypoxemia in Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- PMID: 33469400
- PMCID: PMC7811484
- DOI: 10.2147/NSS.S288618
Nasal Obstruction as a Potential Factor Contributing to Hypoxemia in Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the correlation between nasal resistance and oxygen desaturation to better elucidate the role of nasal obstruction in the pathophysiology of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Patients and methods: Eighty-eight OSA patients aged between 22 and 77 years were enrolled in this study. Nasal resistance was measured at pressures of 75, 150, and 300 Pa, with the patients first in the seated position than in the supine position. Relationships between the oximetric variables and nasal resistance in the seated and supine positions were analyzed.
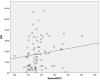
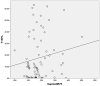
Results: From seated to supine position, a statistically significant increase in nasal resistance was observed at pressures of 75 and 150 Pa (p=0.001 and p=0.006, respectively). Significant positive correlations were noted between nasal resistance in the supine position at 75 Pa (SupineNR75) and oximetry variables, including oxygen desaturation index (ODI, p=0.015) and the percentage of total time with oxygen saturation level lower than 90% (T < 90%, p=0.012). However, significant positive correlations existed only in moderate to severe OSA when the study group was further divided into two subgroups (mild vs moderate to severe OSA). Body mass index (β = 0.476, p<0.001) and SupineNR75 (β = 0.303, p=0.004) were identified as independent predictors for increased ODI.
Conclusion: Nasal resistance in the supine position measured at 75 Pa significantly correlated with the severity of oxygen desaturation. Therefore, nasal obstruction may play an important role in the pathophysiology of hypoxemia in OSA patients, especially in patients with moderate to severe OSA.
Keywords: OSA; nasal resistance; polysomnography; rhinomanometry.
© 2021 Lan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nasal obstruction and sleep-disordered breathing: the effect of supine body position on nasal measurements in snorers.Acta Otolaryngol. 2003 Jun;123(5):648-54. doi: 10.1080/00016480310001493. Acta Otolaryngol. 2003. PMID: 12875589
-
Role of rhinomanometry in the prediction of therapeutic positive airway pressure for obstructive sleep apnea.Respir Res. 2020 May 13;21(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01382-4. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 32404107 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of postural nasal resistance following oropharyngeal surgery in patients with moderate-severe obstructive sleep apnea.Rhinology. 2021 Feb 1;59(1):75-80. doi: 10.4193/Rhin19.331. Rhinology. 2021. PMID: 32779643
-
The Value of Oxygen Desaturation Index for Diagnosing Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review.Laryngoscope. 2021 Feb;131(2):440-447. doi: 10.1002/lary.28663. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Laryngoscope. 2021. PMID: 32333683
-
Anti-inflammatory medications for obstructive sleep apnoea in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 17;1(1):CD007074. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007074.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 31978261 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress in patients with nasal respiratory impairment and OSAS.Sleep Breath. 2025 May 19;29(3):188. doi: 10.1007/s11325-025-03361-9. Sleep Breath. 2025. PMID: 40387971
References
-
- Akhan G, Ayik S, Songu M. Cerebral oxygenation during sleep in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a near-infrared spectroscopy study. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;41(6):437–442. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

