Neurofeedback of Alpha Activity on Memory in Healthy Participants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33469422
- PMCID: PMC7813983
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.562360
Neurofeedback of Alpha Activity on Memory in Healthy Participants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
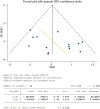
Background: Neurofeedback training (NFT) has recently been proposed as a valuable technique for cognitive enhancement and psychiatric amelioration. However, effect of NFT of alpha activity on memory is controversial. The current study analyzed previous works in terms of randomized and blinded analyses, training paradigms, and participant characteristics to validate the efficacy of alpha NFT on memory in a healthy population. Objectives: A systematic meta-analysis of studies with randomized controlled trials was performed to explore the effect of alpha NFT on working memory (WM) and episodic memory (EM) in a healthy population. Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library from January 1, 1999, to November 30, 2019. Previous studies were evaluated with the Cochrane risk of bias (RoB). A meta-analysis calculating absolute weighted standardized mean difference (SMD) using random-effects models was employed. Heterogeneity was estimated using I 2 statistics. Funnel plots and Egger's test were performed to evaluate the quality of evidence. Results: Sixteen studies with 217 healthy participants in the control group and 210 participants in the alpha group met the eligibility criteria. Alpha NFT studies with WM measures presented little publication bias (P = 0.116), and 5 of 7 domains in the Cochrane RoB exhibited a low risk of bias. The overall effect size from 14 WM studies was 0.56 (95% CI 0.31-0.81, P < 0.0001; I 2 = 28%). Six EM studies exhibited an effect size of 0.77 (95% CI 0.06-1.49, P = 0.03; I 2 = 77%). Conclusion: Meta-analysis results suggest that alpha NFT seems to have a positive effect on the WM and EM of healthy participants. Future efforts should focus on the neurophysiological mechanisms of alpha NFT in memory.
Keywords: alpha; cognition; memory; neurofeedback; randomized controlled trial.
Copyright © 2021 Yeh, Hsueh and Shaw.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative effectiveness of electroencephalogram-neurofeedback training of 3-45 frequency band on memory in healthy population: a network meta-analysis with systematic literature search.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2025 Apr 24;22(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12984-025-01634-8. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40275307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Portable wireless neurofeedback system of EEG alpha rhythm enhances memory.Biomed Eng Online. 2017 Nov 13;16(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12938-017-0418-8. Biomed Eng Online. 2017. PMID: 29132359 Free PMC article.
-
An investigation of the effectiveness of neurofeedback training on motor performance in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Neuroimage. 2023 Apr 15;270:120000. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120000. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Neuroimage. 2023. PMID: 36870431
-
Neurofeedback training of EEG alpha rhythm enhances episodic and working memory.Hum Brain Mapp. 2016 Jul;37(7):2662-75. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23201. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016. PMID: 27038114 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of Polyphenols on Working and Episodic Memory in Non-pathological and Pathological Aging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Nutr. 2022 Jan 26;8:720756. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.720756. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35155509 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Neuro-Feedback Training for PTSD Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 12;19(20):13096. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192013096. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36293673 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of eyes-closed resting alpha amplitude predicting neurofeedback learning of upregulation alpha activity.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 4;11(1):19615. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99235-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34608244 Free PMC article.
-
Neurofeedback and neural self-regulation: a new perspective based on allostasis.Rev Neurosci. 2022 Feb 7;33(6):607-629. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2021-0133. Print 2022 Aug 26. Rev Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35122709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of Electroencephalography Neurofeedback for Improving Working Memory and Episodic Memory in the Elderly: A Meta-Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Feb 22;60(3):369. doi: 10.3390/medicina60030369. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38541096 Free PMC article.
-
Musical Auditory Alpha Wave Neurofeedback: Validation and Cognitive Perspectives.Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2021 Dec;46(4):323-334. doi: 10.1007/s10484-021-09507-1. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2021. PMID: 33929674 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Boynton T. (2001). Applied research using alpha/theta training for enhancing creativity and well-being. J. Neurother. 5, 5–18. 10.1300/J184v05n01_02 - DOI
-
- Cortese S., Ferrin M., Brandeis D., Holtmann M., Aggensteiner P., Daley D., et al. . (2016). Neurofeedback for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: meta-analysis of clinical and neuropsychological outcomes from randomized controlled trials. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 55, 444–455. 10.1016/j.jaac.2016.03.007 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

