Performance Analysis With Different Types of Visual Stimuli in a BCI-Based Speller Under an RSVP Paradigm
- PMID: 33469425
- PMCID: PMC7814000
- DOI: 10.3389/fncom.2020.587702
Performance Analysis With Different Types of Visual Stimuli in a BCI-Based Speller Under an RSVP Paradigm
Abstract
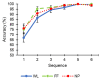
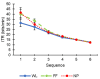
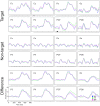
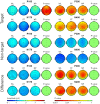
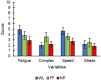
Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) systems enable an alternative communication channel for severely-motor disabled patients to interact with their environment using no muscular movements. In recent years, the importance of research into non-gaze dependent brain-computer interface paradigms has been increasing, in contrast to the most frequently studied BCI-based speller paradigm (i.e., row-column presentation, RCP). Several visual modifications that have already been validated under the RCP paradigm for communication purposes have not been validated under the most extended non-gaze dependent rapid serial visual presentation (RSVP) paradigm. Thus, in the present study, three different sets of stimuli were assessed under RSVP, with the following communication features: white letters (WL), famous faces (FF), neutral pictures (NP). Eleven healthy subjects participated in this experiment, in which the subjects had to go through a calibration phase, an online phase and, finally, a subjective questionnaire completion phase. The results showed that the FF and NP stimuli promoted better performance in the calibration and online phases, being slightly better in the FF paradigm. Regarding the subjective questionnaires, again both FF and NP were preferred by the participants in contrast to the WL stimuli, but this time the NP stimuli scored slightly higher. These findings suggest that the use of FF and NP for RSVP-based spellers could be beneficial to increase information transfer rate in comparison to the most frequently used letter-based stimuli and could represent a promising communication system for individuals with altered ocular-motor function.
Keywords: N170; P300; brain computer-interface (BCI); electroencephalography (EEG); famous faces; neutral pictures; rapid serial visual presentation (RSVP).
Copyright © 2021 Ron-Angevin, Medina-Juliá, Fernández-Rodríguez, Velasco-Álvarez, Andre, Lespinet-Najib and Garcia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Acqualagna L., Treder M. S., Blankertz B. (2013). Chroma speller: isotropic visual stimuli for truly gaze-independent spelling, in International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, NER (San Diego, CA: ), 1041–1044.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

