Accurate detection of Covid-19 patients based on Feature Correlated Naïve Bayes (FCNB) classification strategy
- PMID: 33469467
- PMCID: PMC7809685
- DOI: 10.1007/s12652-020-02883-2
Accurate detection of Covid-19 patients based on Feature Correlated Naïve Bayes (FCNB) classification strategy
Abstract
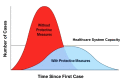
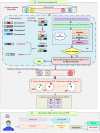
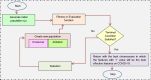
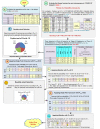
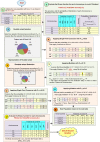
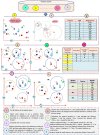
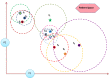
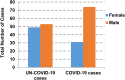
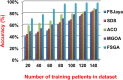
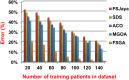
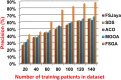
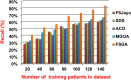
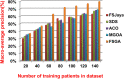
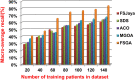
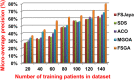
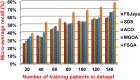
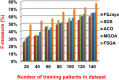
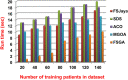
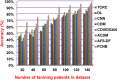
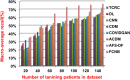
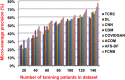
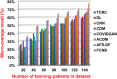
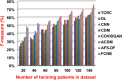
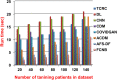
The outbreak of Coronavirus (COVID-19) has spread between people around the world at a rapid rate so that the number of infected people and deaths is increasing quickly every day. Accordingly, it is a vital process to detect positive cases at an early stage for treatment and controlling the disease from spreading. Several medical tests had been applied for COVID-19 detection in certain injuries, but with limited efficiency. In this study, a new COVID-19 diagnosis strategy called Feature Correlated Naïve Bayes (FCNB) has been introduced. The FCNB consists of four phases, which are; Feature Selection Phase (FSP), Feature Clustering Phase (FCP), Master Feature Weighting Phase (MFWP), and Feature Correlated Naïve Bayes Phase (FCNBP). The FSP selects only the most effective features among the extracted features from laboratory tests for both COVID-19 patients and non-COVID-19 people by using the Genetic Algorithm as a wrapper method. The FCP constructs many clusters of features based on the selected features from FSP by using a novel clustering technique. These clusters of features are called Master Features (MFs) in which each MF contains a set of dependent features. The MFWP assigns a weight value to each MF by using a new weight calculation method. The FCNBP is used to classify patients based on the weighted Naïve Bayes algorithm with many modifications as the correlation between features. The proposed FCNB strategy has been compared to recent competitive techniques. Experimental results have proven the effectiveness of the FCNB strategy in which it outperforms recent competitive techniques because it achieves the maximum (99%) detection accuracy.
Keywords: COVID-19; Classification; Correlation; FCNB; Feature selection.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH, DE part of Springer Nature 2021.
Figures
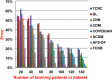
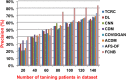
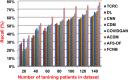
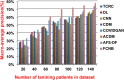
References
-
- Abellán J, Castellano J. Improving the naive bayes classifier via a quick variable selection method using maximum of entropy. Entropy. 2017;19(6):1–17.
-
- Alazab M, Awajan A, Mesleh A, Abraham A, et al. COVID-19 prediction and detection using deep learning. Int J Comput Inf Syst Ind Manag Appl. 2020;12:168–181.
-
- Ali ZH, Ali HA. QoS provisioning framework for service-oriented internet of things (IoT) Clust Comput. 2020;23:575–591.
-
- Arunadevi J, Ganeshamoorthi K, Rampriya R. Application of feature weighting for the intensification of data classification. IJITEE. 2019;9:879–887.
-
- Ayed A, Halima M, Alimi A (2015) Survey on clustering methods: towards fuzzy clustering for big data. In: Proceedings of the 2014 6th international conference of soft computing and pattern recognition (SoCPaR). IEEE, Tunis, Tunisia, pp 331–336
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
