Presence of pyrroloquinazoline alkaloid in Adhatoda vasica attenuates inflammatory response through the downregulation of pro-inflammatory mediators in LPS stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages
- PMID: 33469504
- PMCID: PMC7803918
- DOI: 10.34172/bi.2021.03
Presence of pyrroloquinazoline alkaloid in Adhatoda vasica attenuates inflammatory response through the downregulation of pro-inflammatory mediators in LPS stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages
Abstract
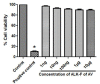
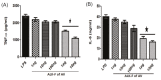
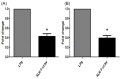
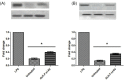
Introduction: Inflammation is the primary response caused due to harmful stimuli which are followed by the increased draining of plasma and immune cells from the body into the site of the injured tissue. A signaling cascade of growth factors and cytokines propagates and eventually matures in the inflammatory site involving the blood vessels and immune markers within the injured tissue in order to promote the renewal of the degenerated tissue. During a chronic disorder like diabetic foot ulcer, there is an obstinate inflammation which may act as a prime factor for limb amputation and upon persistent prevalence may even lead to death. Methods: This study focuses on the mode of action of ALK-F (alkaloid fraction) isolated from Adhatoda vasica in attenuating the nitric oxide production which was estimated by Griess assay, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) expression was analyzed by ELISA and expression of COX-2 and iNOS by RT-PCR and western blotting in LPS stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Total intracellular ROS was analyzed by DCFH-DA probing and the presence of quinazoline alkaloid (vasicine) in the ALK-F was evidenced by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Results: The ALK-F of A. vasica exhibited a significant inhibitory effect on LPS elicited nitrite production (13.2 ± 1.06 µM), iNOS, and COX-2 (2.6 and 3.3 fold) in a dose-dependent manner. There was a significant decrease in the generation of these pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α (1102 ± 1.02 pg/mL) and IL-6 (18 ± 0.87 ng/mL) and total intracellular ROS in the highest tested concentrations (1 µg and 10 µg) of ALK-F of A. vasica. HPLC analysis by the gradient elution method revealed the presence of 12% of quinazoline alkaloid vasicine in the crude alkaloid fraction. Conclusion: Thus this study communally suggests that attenuation of nitric oxide and the dysregulation of genes responsible for inflammation which deliberates A. vasica to conflict against inflammation and provide remedial benefits in diabetic wound care.
Keywords: Cyclooxygenases-2; Diabetic foot ulcer; Inducible nitric oxide synthase; Limb amputation; Lipopolysaccharide; Quinazoline alkaloids; RAW 264.7 macrophages.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials