Parallel reaction pathways accelerate folding of a guanine quadruplex
- PMID: 33469659
- PMCID: PMC7897495
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1286
Parallel reaction pathways accelerate folding of a guanine quadruplex
Abstract
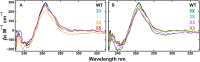
G-quadruplexes (G4s) are four-stranded, guanine-rich nucleic acid structures that can influence a variety of biological processes such as the transcription and translation of genes and DNA replication. In many cases, a single G4-forming nucleic acid sequence can adopt multiple different folded conformations that interconvert on biologically relevant timescales, entropically stabilizing the folded state. The coexistence of different folded conformations also suggests that there are multiple pathways leading from the unfolded to the folded state ensembles, potentially modulating the folding rate and biological activity. We have developed an experimental method for quantifying the contributions of individual pathways to the folding of conformationally heterogeneous G4s that is based on mutagenesis, thermal hysteresis kinetic experiments and global analysis, and validated our results using photocaged kinetic NMR experiments. We studied the regulatory Pu22 G4 from the c-myc oncogene promoter, which adopts at least four distinct folded isomers. We found that the presence of four parallel pathways leads to a 2.5-fold acceleration in folding; that is, the effective folding rate from the unfolded to folded ensembles is 2.5 times as large as the rate constant for the fastest individual pathway. Since many G4 sequences can adopt many more than four isomers, folding accelerations of more than an order of magnitude are possible via this mechanism.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


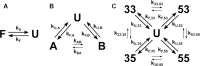

Similar articles
-
High Mechanical Stability and Slow Unfolding Rates Are Prevalent in Parallel-Stranded DNA G-Quadruplexes.J Phys Chem Lett. 2020 Oct 1;11(19):7966-7971. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c02229. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Phys Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32885976
-
Thermodynamic stability and folding kinetics of the major G-quadruplex and its loop isomers formed in the nuclease hypersensitive element in the human c-Myc promoter: effect of loops and flanking segments on the stability of parallel-stranded intramolecular G-quadruplexes.Biochemistry. 2010 Nov 2;49(43):9152-60. doi: 10.1021/bi100946g. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20849082 Free PMC article.
-
The Folding Landscapes of Human Telomeric RNA and DNA G-Quadruplexes are Markedly Different.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 May 3;60(19):10895-10901. doi: 10.1002/anie.202100280. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 33539622 Free PMC article.
-
Multimeric G-quadruplexes: A review on their biological roles and targeting.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Apr 15;204:89-102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.197. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 35124022 Review.
-
Structure of the biologically relevant G-quadruplex in the c-MYC promoter.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2006;25(8):951-68. doi: 10.1080/15257770600809913. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2006. PMID: 16901825 Review.
Cited by
-
Frustrated folding of guanine quadruplexes in telomeric DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Apr 6;49(6):3063-3076. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab140. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33693924 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Polymorphism of Guanine Quadruplex-Containing Regions in Human Promoters.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 16;23(24):16020. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416020. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555662 Free PMC article.
-
Iso-FRET: an isothermal competition assay to analyze quadruplex formation in vitro.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Sep 9;50(16):e93. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac465. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35670668 Free PMC article.
-
Developments in solution-state NMR yield broader and deeper views of the dynamic ensembles of nucleic acids.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021 Oct;70:16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2021.02.007. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021. PMID: 33836446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-quadruplexes as pivotal components of cis-regulatory elements in the human genome.BMC Biol. 2024 Aug 26;22(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01971-5. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39183303 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

