SARS-CoV-2/human interactome reveals ACE2 locus crosstalk with the immune regulatory network in the host
- PMID: 33469663
- PMCID: PMC7928900
- DOI: 10.1093/femspd/ftab005
SARS-CoV-2/human interactome reveals ACE2 locus crosstalk with the immune regulatory network in the host
Abstract
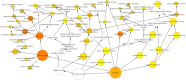
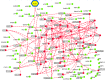
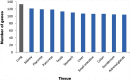
Severe acute respiratory syndrome, coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), remains to be a threat across the globe. SARS-CoV-2 entry into the host is mediated by binding of viral spike protein to the Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor. ACE2 is an essential member of the Renin-Angiotensin system (RAS) involved in maintaining the blood pressure and vascular remodelling. Although ACE2 receptor is the entry point to the host, recent studies show activation of ACE2 to modulate the host to develop a suitable environment for its replication. However, the ACE2 activating the immune signals on SARS-CoV-2 attachment is still under investigation. We have used systems biological approach to construct the host regulatory network upon SARS-CoV-2 attachment to the ACE2 receptor. Since lungs are the primary infection site, we integrate human lung gene expression profile along with the host regulatory network to demonstrate the altered host signalling mechanism in viral infection. Further, the network was functionally enriched to determine immune modulation in the network. We also used the proteomic database to assess the occurrence of similar signalling events in other human tissues that exhibit lineage of infection across different organs. The constructed network contains 133 host proteins with 298 interactions that directly or indirectly connect to the ACE2 receptor. Among 133 proteins, 29 were found to be differentially regulated in the host lungs on SARS-CoV-2 infection. Altered proteins connect multiple proteins in a network that modulates kinase, carboxypeptidase and cytokine activity, leading to changes in the host immune system, cell cycle and signal transduction mechanisms. Further investigation showed the presence of similar signalling events in the kidneys, placenta, pancreas, testis, small intestine and adrenal gland as well. Overall, our results will help in understanding the immune molecular regulatory networks influenced by the ACE2 mediated interaction in other body tissues, which may aid in identifying the secondary health complications associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: ACE2/AGT-axis; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; immune response.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 Cellular Entry Is Independent of the ACE2 Cytoplasmic Domain Signaling.Cells. 2021 Jul 17;10(7):1814. doi: 10.3390/cells10071814. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34359983 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial and Endothelial Expressions of ACE2: SARS-CoV-2 Entry Routes.J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2021;24:84-93. doi: 10.18433/jpps31455. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 33626315 Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2, ACE2 expression, and systemic organ invasion.Physiol Genomics. 2021 Feb 1;53(2):51-60. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00087.2020. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Physiol Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33275540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin type II blockers with ACE2 overexpression in COVID-19 comorbidities: A pathway-based analytical study.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 5;896:173899. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173899. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33508281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACE2: from protection of liver disease to propagation of COVID-19.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Dec 11;134(23):3137-3158. doi: 10.1042/CS20201268. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 33284956 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular signaling pathways, pathophysiological features in various organs, and treatment strategies in SARS-CoV2 infection.Acta Histochem. 2022 Jul;124(5):151908. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2022.151908. Epub 2022 May 25. Acta Histochem. 2022. PMID: 35662001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Looking at COVID-19 from a Systems Biology Perspective.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 22;12(2):188. doi: 10.3390/biom12020188. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 infection: from stress-related cortisol levels to adrenal glands infarction.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2022 Jan-Mar;63(1):39-48. doi: 10.47162/RJME.63.1.03. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2022. PMID: 36074666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive proteomic analysis of HCoV-OC43 virions and virus-modulated extracellular vesicles.J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0085024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00850-24. Epub 2024 Jul 2. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38953378 Free PMC article.
-
Acute kidney injury associated to COVID-19 leads to a strong unbalance of circulant immune mediators.Cytokine. 2022 Sep;157:155974. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155974. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Cytokine. 2022. PMID: 35907365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baatar D, Patel K, Taub DD. The effects of ghrelin on inflammation and the immune system. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011;340:44–58. - PubMed
-
- Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo Aet al. . Features, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19). In: Statpearls [internet]. StatPearls Publishing. 2, 2020. - PubMed
-
- Cheng ZJ, Vapaatalo H, Mervaala E. Angiotensin II and vascular inflammation. Med Sci Monit. 2005;11:RA194–205. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

