Using advanced statistical tools to assess the impact of a small landfill site on the aquatic environment
- PMID: 33469715
- PMCID: PMC7815553
- DOI: 10.1007/s10661-021-08850-4
Using advanced statistical tools to assess the impact of a small landfill site on the aquatic environment
Abstract
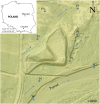
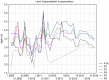
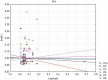
The aim of the study was to assess the impact of a small municipal landfill on the aquatic environment over 9 years, using advanced statistical tools. The results of the study of surface, ground- and leachate waters from 2008 to 2016 were subjected to detailed statistical analysis based on 15 physicochemical indicators. Factor analysis accounted for the requirements of the WHO, the European Union and the nation of Poland using 8 statistical analytical methods. The analysis of leachate contamination from the landfill site with the use of advanced statistical tools revealed its interaction with groundwater. The assessment was based on increased and statistically significant values and correlations of temperature, Zn and N-NO3 between leachate and groundwater, factors demonstrating the negative impact of the landfill. In the case of Zn, there was also a correlation between the tested waters below the landfill. The increased PAH values in the examined surface and ground waters were not a consequence of waste disposal. However, the deterioration of the chemical state of groundwater in the vicinity of the landfill could result from a certain dysfunction of the facility's infrastructure after operating for more than 20 years.
Keywords: Advanced statistical analysis; Impact; Landfill; Leachate; Municipal waste; Water.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Assessment of the impact of a non-operational municipal landfill site on groundwater quality: a case study from southwestern Poland.Environ Monit Assess. 2025 Jul 8;197(8):872. doi: 10.1007/s10661-025-14280-3. Environ Monit Assess. 2025. PMID: 40624353 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of small municipal solid waste landfill on groundwater quality.Environ Monit Assess. 2019 Feb 19;191(3):169. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7279-5. Environ Monit Assess. 2019. PMID: 30778777 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-indicator analysis of the influence of old municipal landfill sites on the aquatic environment: case study.Environ Monit Assess. 2019 Nov 26;191(12):773. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7814-4. Environ Monit Assess. 2019. PMID: 31773284 Free PMC article.
-
A review of groundwater contamination near municipal solid waste landfill sites in China.Sci Total Environ. 2016 Nov 1;569-570:1255-1264. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.201. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Sci Total Environ. 2016. PMID: 27387811 Review.
-
Effect of landfill leachate on arsenic migration and transformation in shallow groundwater systems.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Jan;31(4):5032-5042. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-31629-8. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38148459 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the impact of a non-operational municipal landfill site on groundwater quality: a case study from southwestern Poland.Environ Monit Assess. 2025 Jul 8;197(8):872. doi: 10.1007/s10661-025-14280-3. Environ Monit Assess. 2025. PMID: 40624353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abiriga D, Vestgarden LS, Klempe H. Groundwater contamination from a municipal landfill: effect of age, landfill closure, and season on groundwater chemistry. Science of the Total Environment. 2020;737:140307. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed AM, Sulaiman WN. Evaluation groundwater and soil pollution in a landfill area using electrical resistivity imaging survey. Environmental Management. 2001;28(5):655–663. - PubMed
-
- Al-Yaqout A, Hamoda MF. Long-term temporal variations in characteristics of leachates from a closed landfill in an arid region. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution. 2020;231:319.
-
- APHA . Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater. USA: In American public health association. Washington; 2007.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

