Autopsy findings after long-term treatment of COVID-19 patients with microbiological correlation
- PMID: 33471172
- PMCID: PMC7816067
- DOI: 10.1007/s00428-020-03014-0
Autopsy findings after long-term treatment of COVID-19 patients with microbiological correlation
Abstract
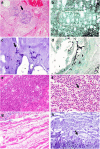
Between April and June 2020, i.e., during the first wave of pandemic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), 55 patients underwent long-term treatment in the intensive care unit at the University Hospital of Regensburg. Most of them were transferred from smaller hospitals, often due to the need for an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation system. Autopsy was performed in 8/17 COVID-19-proven patients after long-term treatment (mean: 33.6 days). Autopsy revealed that the typical pathological changes occurring during the early stages of the disease (e.g., thrombosis, endothelitis, capillaritis) are less prevalent at this stage, while severe diffuse alveolar damage and especially coinfection with different fungal species were the most conspicuous finding. In addition, signs of macrophage activation syndrome was detected in 7 of 8 patients. Thus, fungal infections were a leading cause of death in our cohort of severely ill patients and may alter clinical management of patients, particularly in long-term periods of treatment.
Keywords: Autopsy; COVID-19; Fungal infection; Macrophage activation syndrome; Mycosis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Cabaret O, Toussain G, Abermil N, Alsamad IA, Botterel F, Costa JM, Papon JF, Bretagne S. Degradation of fungal DNA in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sinus fungal balls hampers reliable sequence-based identification of fungi. Medical mycology. 2011;49:329–332. doi: 10.3109/13693786.2010.525537. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

