In vivo antagonistic role of the Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 regulatory proteins Tax and HBZ
- PMID: 33471856
- PMCID: PMC7817025
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009219
In vivo antagonistic role of the Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 regulatory proteins Tax and HBZ
Abstract
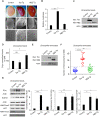
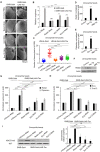
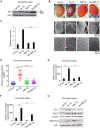
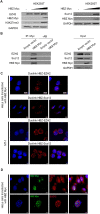
Adult T cell leukemia (ATL) is an aggressive malignancy secondary to chronic infection by the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infection. Two viral proteins, Tax and HBZ, play central roles in ATL leukemogenesis. Tax expression transforms T cells in vitro and induces ATL-like disease in mice. Tax also induces a rough eye phenotype and increases hemocyte count in Drosophila melanogaster, indicative of transformation. Among multiple functions, Tax modulates the expression of the enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2), a methyltransferase of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2), leading to H3K27me3-dependent reprogramming of around half of cellular genes. HBZ is a negative regulator of Tax-mediated viral transcription. HBZ effects on epigenetic signatures are underexplored. Here, we established an hbz transgenic fly model, and demonstrated that, unlike Tax, which induces NF-κB activation and enhanced PRC2 activity creating an activation loop, HBZ neither induces transformation nor NF-κB activation in vivo. However, overexpression of Tax or HBZ increases the PRC2 activity and both proteins directly interact with PRC2 complex core components. Importantly, overexpression of HBZ in tax transgenic flies prevents Tax-induced NF-κB or PRC2 activation and totally rescues Tax-induced transformation and senescence. Our results establish the in vivo antagonistic effect of HBZ on Tax-induced transformation and cellular effects. This study helps understanding long-term HTLV-1 persistence and cellular transformation and opens perspectives for new therapeutic strategies targeting the epigenetic machinery in ATL.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Basic Leucine Zipper Factor Attenuates Repair of Double-Stranded DNA Breaks via Nonhomologous End Joining.J Virol. 2018 Jul 17;92(15):e00672-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00672-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29769340 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Interactions between the Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Antisense Protein HBZ and the SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Family: Implications for Viral Life Cycle.J Virol. 2019 Jul 30;93(16):e00412-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00412-19. Print 2019 Aug 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31142665 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of human T-lymphotropic virus type I latency and reactivation by HBZ and Rex.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Apr 3;10(4):e1004040. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004040. eCollection 2014 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24699669 Free PMC article.
-
Adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma as a viral disease: Subtypes based on viral aspects.Cancer Sci. 2021 May;112(5):1688-1694. doi: 10.1111/cas.14869. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33630351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma-A Tale of Two Proteins: Tax and HBZ.Viruses. 2016 Jun 16;8(6):161. doi: 10.3390/v8060161. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27322308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of HTLV-1 infection and progression biomarkers: An overview.Braz J Infect Dis. 2021 May-Jun;25(3):101594. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2021.101594. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Braz J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34256025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HTLV-1 Infection and Pathogenesis: New Insights from Cellular and Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 27;22(15):8001. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158001. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between innate immunity and the viral oncoproteins Tax and HBZ in the pathogenesis and therapeutic response of HTLV-1 associated adult T cell leukemia.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 22;13:957535. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.957535. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35935975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral oncogenesis in cancer: from mechanisms to therapeutics.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 May 12;10(1):151. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02197-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40350456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary cells from patients with adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma depend on HTLV-1 Tax expression for NF-κB activation and survival.Blood Cancer J. 2023 May 3;13(1):67. doi: 10.1038/s41408-023-00841-7. Blood Cancer J. 2023. PMID: 37137914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hinuma Y, Komoda H, Chosa T, Kondo T, Kohakura M, Takenaka T, et al. Antibodies to adult T-cell leukemia-virus-associated antigen (ATLA) in sera from patients with ATL and controls in Japan: a nation-wide sero-epidemiologic study. International journal of cancer. 1982;29(6):631–5. 10.1002/ijc.2910290606 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

