Benzalkonium Chloride Disinfectants Induce Apoptosis, Inhibit Proliferation, and Activate the Integrated Stress Response in a 3-D in Vitro Model of Neurodevelopment
- PMID: 33472002
- PMCID: PMC8131244
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.0c00386
Benzalkonium Chloride Disinfectants Induce Apoptosis, Inhibit Proliferation, and Activate the Integrated Stress Response in a 3-D in Vitro Model of Neurodevelopment
Abstract
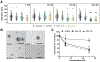
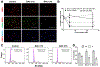
We previously found that the widely used disinfectants, benzalkonium chlorides (BACs), alter cholesterol and lipid homeostasis in neuronal cell lines and in neonatal mouse brains. Here, we investigate the effects of BACs on neurospheres, an in vitro three-dimensional model of neurodevelopment. Neurospheres cultured from mouse embryonic neural progenitor cells (NPCs) were exposed to increasing concentrations (from 1 to 100 nM) of a short-chain BAC (BAC C12), a long-chain BAC (BAC C16), and AY9944 (a known DHCR7 inhibitor). We found that the sizes of neurospheres were decreased by both BACs but not by AY9944. Furthermore, we observed potent inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis at the step of DHCR7 by BAC C12 but not by BAC C16, suggesting that cholesterol biosynthesis inhibition is not responsible for the observed reduction in neurosphere growth. By using immunostaining and cell cycle analysis, we found that both BACs induced apoptosis and decreased proliferation of NPCs. To explore the mechanisms underlying their effect on neurosphere growth, we carried out RNA sequencing on neurospheres exposed to each BAC at 50 nM for 24 h, which revealed the activation of the integrated stress response by both BACs. Overall, these results suggest that BACs affect neurodevelopment by inducing the integrated stress response in a manner independent of their effects on cholesterol biosynthesis.
Figures



References
-
- Gilbert P; Moore LE, Cationic antiseptics: diversity of action under a common epithet. J. Appl. Microbiol 2005, 99 (4), 703–15. - PubMed
-
- US FDA, Safety and Effectiveness of Health Care Antiseptics; Topical Antimicrobial Drug Products for Over-the-Counter Human Use; Proposed Amendment of the Tentative Final Monograph; Reopening of Administrative Record. Federal Register 2015, 21 CFR Part 310, 80 (84), 25165–25205.
-
- US FDA, Safety and Effectiveness of Consumer Antiseptics; Topical Antimicrobial Drug Products for Over-the-Counter Human Use; Proposed Amendment of the Tentative Final Monograph; Reopening of Administrative Record Federal Register 2016, 21 CFR Part 310, 81 (126), 42911–42937. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez M; Jégu J; Kopferschmitt MC; Donnay C; Hedelin G; Matzinger F; Velten M; Guilloux L; Cantineau A; de Blay F, Asthma among workers in healthcare settings: role of disinfection with quaternary ammonium compounds. Clin Exp Allergy 2014, 44 (3), 393–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

