Systematic comparison of high-throughput single-cell RNA-seq methods for immune cell profiling
- PMID: 33472597
- PMCID: PMC7818754
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-020-07358-4
Systematic comparison of high-throughput single-cell RNA-seq methods for immune cell profiling
Abstract
Background: Elucidation of immune populations with single-cell RNA-seq has greatly benefited the field of immunology by deepening the characterization of immune heterogeneity and leading to the discovery of new subtypes. However, single-cell methods inherently suffer from limitations in the recovery of complete transcriptomes due to the prevalence of cellular and transcriptional dropout events. This issue is often compounded by limited sample availability and limited prior knowledge of heterogeneity, which can confound data interpretation.
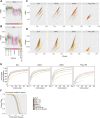
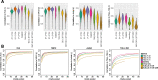
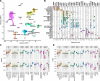
Results: Here, we systematically benchmarked seven high-throughput single-cell RNA-seq methods. We prepared 21 libraries under identical conditions of a defined mixture of two human and two murine lymphocyte cell lines, simulating heterogeneity across immune-cell types and cell sizes. We evaluated methods by their cell recovery rate, library efficiency, sensitivity, and ability to recover expression signatures for each cell type. We observed higher mRNA detection sensitivity with the 10x Genomics 5' v1 and 3' v3 methods. We demonstrate that these methods have fewer dropout events, which facilitates the identification of differentially-expressed genes and improves the concordance of single-cell profiles to immune bulk RNA-seq signatures.
Conclusion: Overall, our characterization of immune cell mixtures provides useful metrics, which can guide selection of a high-throughput single-cell RNA-seq method for profiling more complex immune-cell heterogeneity usually found in vivo.
Keywords: High throughput sequencing; Immune-cell profiling; Single cell; Single-cell RNA-seq; Transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal’s policy and have the following conflicts: Tracy M. Yamawaki, Daniel R. Lu, Daniel C. Ellwanger, Dev Bhatt, Paolo Manzanillo, Vanessa, Arias, Hong Zhou, Oliver Homann, Songli Wang, and Chi-Ming Li are employees or contract workers at Amgen Inc. Oh Kyu Yoon was employed by Amgen Inc. while working on the study. All authors owned Amgen shares when the experiments were carried out. However, these do not alter the authors’ adherence to all journal policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures





References
-
- Bandura DR, Baranov VI, Ornatsky OI, Antonov A, Kinach R, Lou X, Pavlov S, Vorobiev S, Dick JE, Tanner SD. Mass cytometry: technique for real time single cell multitarget immunoassay based on inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2009;81(16):6813–6822. doi: 10.1021/ac901049w. - DOI - PubMed
-
- He H, Suryawanshi H, Morozov P, Gay-Mimbrera J, Del Duca E, Kim HJ, Kameyama N, Estrada Y, Der E, Krueger JG, et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis of human skin identifies novel fibroblast subpopulation and enrichment of immune subsets in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145(6):1615–28.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

