Update on biology and management of mesothelioma
- PMID: 33472960
- PMCID: PMC9489032
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0226-2020
Update on biology and management of mesothelioma
Abstract
Malignant pleural mesothelioma is an aggressive, incurable cancer that is usually caused by asbestos exposure several decades before symptoms arise. Despite widespread prohibition of asbestos production and supply, its incidence continues to increase. It is heterogeneous in its presentation and behaviour, and diagnosis can be notoriously difficult. Identification of actionable gene mutations has proven challenging and current treatment options are largely ineffective, with a median survival of 10-12 months.However, the past few years have witnessed major advances in our understanding of the biology and pathogenesis of mesothelioma. This has also revealed the limitations of existing diagnostic algorithms and identified new treatment targets.Recent clinical trials have re-examined the role of surgery, provided new options for the management of associated pleural effusions and heralded the addition of targeted therapies. The increasing complexity of mesothelioma management, along with a desperate need for further research, means that a multidisciplinary team framework is essential for the delivery of contemporary mesothelioma care.This review provides a synthesised overview of the current state of knowledge and an update on the latest research in the field.
Copyright ©ERS 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: R. Asciak has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: V. George reports personal fees from Teva UK Ltd/Haymarket Media Group Ltd, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: N.M. Rahman has nothing to disclose.
Figures
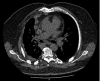
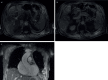
References
-
- Royal College of Physicians (RCP) . National Mesothelioma Audit report 2018 (audit period 2014–16). London, RCP, 2018. www.rcplondon.ac.uk/projects/outputs/national-mesothelioma-audit-report-... Date last accessed: June 30, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
