Molecular determinants and mechanism for antibody cocktail preventing SARS-CoV-2 escape
- PMID: 33473140
- PMCID: PMC7817669
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20789-7
Molecular determinants and mechanism for antibody cocktail preventing SARS-CoV-2 escape
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Molecular determinants and mechanism for antibody cocktail preventing SARS-CoV-2 escape.Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 1;12(1):4177. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24440-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34210985 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Antibody cocktails represent a promising approach to prevent SARS-CoV-2 escape. The determinants for selecting antibody combinations and the mechanism that antibody cocktails prevent viral escape remain unclear. We compared the critical residues in the receptor-binding domain (RBD) used by multiple neutralizing antibodies and cocktails and identified a combination of two antibodies CoV2-06 and CoV2-14 for preventing viral escape. The two antibodies simultaneously bind to non-overlapping epitopes and independently compete for receptor binding. SARS-CoV-2 rapidly escapes from individual antibodies by generating resistant mutations in vitro, but it doesn't escape from the cocktail due to stronger mutational constraints on RBD-ACE2 interaction and RBD protein folding requirements. We also identified a conserved neutralizing epitope shared between SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV for antibody CoV2-12. Treatments with CoV2-06 and CoV2-14 individually and in combination confer protection in mice. These findings provide insights for rational selection and mechanistic understanding of antibody cocktails as candidates for treating COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
Z.K., N.Z., Z.A., X.X., and P.-Y.S. have filed a patent on the reverse genetic system and reporter SARS-CoV-2. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

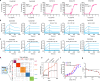



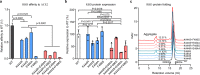


References
-
- Sanders, J. M., Monogue, M. L., Jodlowski, T. Z. & Cutrell, J. B. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA323, 1824–1836 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

