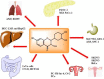
Fisetin: An anticancer perspective
- PMID: 33473265
- PMCID: PMC7802565
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.1872
Fisetin: An anticancer perspective
Abstract
Despite the provision of safe and cost-effective chemopreventive cancer approaches, still there are requirements to enhance their efficiency. The use of dietary agents as phytochemicals plays an imperative role against different human cancer cell lines. Among these novel dietary agents, fisetin (3,3',4',7-tetrahydroxyflavone) is present in different fruits and vegetables such as apple, persimmon, grape, strawberry, cucumber, and onion. Being a potent anticancer agent, fisetin has been used to inhibit stages in the cancer cells (proliferation, invasion), prevent cell cycle progression, inhibit cell growth, induce apoptosis, cause polymerase (PARP) cleavage, and modulate the expressions of Bcl-2 family proteins in different cancer cell lines (HT-29, U266, MDA-MB-231, BT549, and PC-3M-luc-6), respectively. Further, fisetin also suppresses the activation of the PKCα/ROS/ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways, reduces the NF-κB activation, and down-regulates the level of the oncoprotein securin. Fisetin also inhibited cell division and proliferation and invasion as well as lowered the TET1 expression levels. The current review article highlights and discusses the anticancer role of fisetin in cell cultures and animal and human studies. Conclusively, fisetin as a polyphenol with pleiotropic pharmacological properties showed promising anticancer activity in a wide range of cancers. Fisetin suppresses the cancer cell stages, prevents progression in cell cycle and cell growth, and induces apoptosis.
Keywords: anticancer; breast cancer; chemopreventive agent; fisetin; flavonoids.
© 2020 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fisetin regulates TPA-induced breast cell invasion by suppressing matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation via the PKC/ROS/MAPK pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 5;764:79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.06.038. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26101063
-
Fisetin inhibits laryngeal carcinoma through regulation of AKT/NF-κB/mTOR and ERK1/2 signaling pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;83:1164-1174. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.08.035. Epub 2016 Aug 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27551764
-
Fisetin: a dietary antioxidant for health promotion.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Jul 10;19(2):151-62. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4901. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 23121441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the molecular targets of dietary flavonoid fisetin in cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2016 Oct;40-41:130-140. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 May 6. Semin Cancer Biol. 2016. PMID: 27163728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary flavonoid fisetin targets caspase-3-deficient human breast cancer MCF-7 cells by induction of caspase-7-associated apoptosis and inhibition of autophagy.Int J Oncol. 2012 Feb;40(2):469-78. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1203. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21922137
Cited by
-
Antiproliferative Mechanisms of a Polyphenolic Combination of Kaempferol and Fisetin in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 29;24(7):6393. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076393. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047366 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Fisetin-Encapsulated β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges for Breast Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 12;15(5):1480. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051480. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242722 Free PMC article.
-
Fisetin as a chemoprotective and chemotherapeutic agent: mechanistic insights and future directions in cancer therapy.Med Oncol. 2025 Mar 12;42(4):104. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02664-x. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40074915 Review.
-
Fisetin Attenuates Arsenic-Induced Hepatic Damage by Improving Biochemical, Inflammatory, Apoptotic, and Histological Profile: In Vivo and In Silico Approach.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Oct 20;2022:1005255. doi: 10.1155/2022/1005255. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36310620 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Products in Precision Oncology: Plant-Based Small Molecule Inhibitors of Protein Kinases for Cancer Chemoprevention.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 27;15(5):1192. doi: 10.3390/nu15051192. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36904191 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous