The plastid genome of Vanillon (Vanilla pompona, Orchidaceae)
- PMID: 33473949
- PMCID: PMC7800859
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2017.1383201
The plastid genome of Vanillon (Vanilla pompona, Orchidaceae)
Abstract
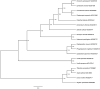
This study presents the complete sequence of Vanilla pompona chloroplast genome. This 148,009 bp long genome consist of 107 genes out of which 30 of them are tRNA, 4 rRNA. Fairly long inverted repeat regions (IR) and large single-copy (LSC) of length 29,807 and 86,358 bp, respectively, were detected. This means an exceptionally short single-copy (SSC) region with only 2037 bp. This truncation of the SSC is due to multiple translocation of ndh genes to the mitochondrion as in majority of the Orchidaceae and especially in the genus Vanilla. The phylogeny presented here meaningfully places Vanillon within the orchid family.
Keywords: Chloroplast genome; de novo assembly; genome skimming; phylogenomics; plastid evolution.
© 2017 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors claim no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bory S, Lubinsky P, Risterucci A-M, Noyer J-L, Grisoni M, Duval M-F, Besse P.. 2008. Patterns of introduction and diversification of Vanilla planifolia (Orchidaceae) in Reunion Island (Indian Ocean). Am J Bot. 95:805–815. - PubMed
-
- Ehlers D, Pfister M.. 1997. Compounds of Vanillons (Vanilla pompona Schiede). J Ess Oil Res. 9:427–431.
-
- FAOSTAT 2017. FAO statistical databases. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. [accessed 2017 Sep 1]. http://www.fao.org
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources