Advances in anti-BRAF therapies for lung cancer
- PMID: 33474634
- PMCID: PMC8068629
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-021-01068-8
Advances in anti-BRAF therapies for lung cancer
Erratum in
-
Author Correction to: Advances in anti-BRAF therapies for lung cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2021 Oct;39(5):1456. doi: 10.1007/s10637-021-01092-8. Invest New Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33646490 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
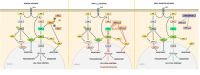
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is one of the most frequent causes of mortality in the western world. v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (BRAF) is a member of the Raf kinase family and plays a critical role in cellular growth, proliferation, and differentiation through the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. The incidence of BRAF mutations in NSCLC is low, accounting for 0-3% of all cases of lung cancer. Given the results obtained in metastatic melanoma, several studies have reported the efficacy of anti-BRAF therapies in NSCLC treatment. In this review, we describe changes in the landscape of BRAF-mutated lung cancer treatment and analyze insights from major clinical trials in the context of future therapeutic prospects.
Keywords: BRAF; Lung cancer; V600.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Association, A. M. (2020) Systemic Therapy for Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review 322, 764–774. - PubMed
-
- Howlader N et al (2019) SEER Cancer statistics review, 1975-2016. National Cancer Institute
-
- Garon EB, Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, Carcereny E, Leighl NB, Ahn MJ, Eder JP, Balmanoukian AS, Aggarwal C, Horn L, Patnaik A, Gubens M, Ramalingam SS, Felip E, Goldman JW, Scalzo C, Jensen E, Kush DA, Hui R. Five-year overall survival for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab: results from the phase i KEYNOTE-001 study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:2518–2527. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00934. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

