Enhancement strategies for transdermal drug delivery systems: current trends and applications
- PMID: 33474709
- PMCID: PMC7817074
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-021-00909-6
Enhancement strategies for transdermal drug delivery systems: current trends and applications
Abstract
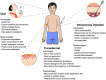
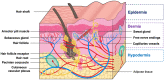
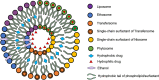
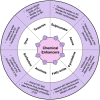
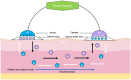
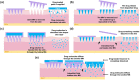
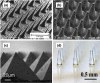
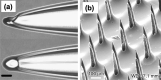
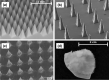
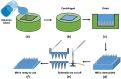
Transdermal drug delivery systems have become an intriguing research topic in pharmaceutical technology area and one of the most frequently developed pharmaceutical products in global market. The use of these systems can overcome associated drawbacks of other delivery routes, such as oral and parenteral. The authors will review current trends, and future applications of transdermal technologies, with specific focus on providing a comprehensive understanding of transdermal drug delivery systems and enhancement strategies. This article will initially discuss each transdermal enhancement method used in the development of first-generation transdermal products. These methods include drug/vehicle interactions, vesicles and particles, stratum corneum modification, energy-driven methods and stratum corneum bypassing techniques. Through suitable design and implementation of active stratum corneum bypassing methods, notably microneedle technology, transdermal delivery systems have been shown to deliver both low and high molecular weight drugs. Microneedle technology platforms have proven themselves to be more versatile than other transdermal systems with opportunities for intradermal delivery of drugs/biotherapeutics and therapeutic drug monitoring. These have shown that microneedles have been a prospective strategy for improving transdermal delivery systems.
Keywords: Active; Enhancement methods; Microneedles; Passive; Skin; Transdermal drug delivery.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ryan Donnelly is an inventor of patents that have been licensed to companies developing microneedle-based products and is a paid advisor to companies developing microneedle-based products. The resulting potential conflict of interest has been disclosed and is managed by Queen’s University Belfast. The companies had no role in the design of the manuscript, in the collection, analyses or interpretation of the various studies reviewed, in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish.
Figures











References
-
- Raj GM, Raveendran R. Introduction to basics of pharmacology and toxicology. 1st vol. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2019.
-
- Marschütz MK, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Oral peptide drug delivery: polymer-inhibitor conjugates protecting insulin from enzymatic degradation in vitro. Biomaterials. 2000;21:1499–1507. - PubMed
-
- McDonald TA, Zepeda ML, Tomlinson MJ, Bee WH, Ivens IA. Subcutaneous administration of biotherapeutics: current experience in animal models. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2010;12:461–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

