ADOPT: automatic deep learning and optimization-based approach for detection of novel coronavirus COVID-19 disease using X-ray images
- PMID: 33475019
- PMCID: PMC7832390
- DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1875049
ADOPT: automatic deep learning and optimization-based approach for detection of novel coronavirus COVID-19 disease using X-ray images
Abstract
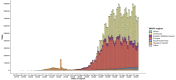
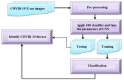
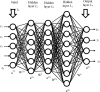
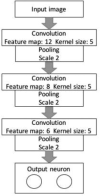
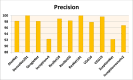
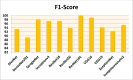
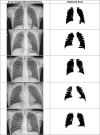
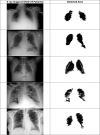
In the hospital, because of the rise in cases daily, there are a small number of COVID-19 test kits available. For this purpose, a rapid alternative diagnostic choice to prevent COVID-19 spread among individuals must be implemented as an automatic detection method. In this article, the multi-objective optimization and deep learning-based technique for identifying infected patients with coronavirus using X-rays is proposed. J48 decision tree approach classifies the deep feature of corona affected X-ray images for the efficient detection of infected patients. In this study, 11 different convolutional neural network-based (CNN) models (AlexNet, VGG16, VGG19, GoogleNet, ResNet18, ResNet50, ResNet101, InceptionV3, InceptionResNetV2, DenseNet201 and XceptionNet) are developed for detection of infected patients with coronavirus pneumonia using X-ray images. The efficiency of the proposed model is tested using k-fold cross-validation method. Moreover, the parameters of CNN deep learning model are tuned using multi-objective spotted hyena optimizer (MOSHO). Extensive analysis shows that the proposed model can classify the X-ray images at a good accuracy, precision, recall, specificity and F1-score rates. Extensive experimental results reveal that the proposed model outperforms competitive models in terms of well-known performance metrics. Hence, the proposed model is useful for real-time COVID-19 disease classification from X-ray chest images.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Keywords: CNN; COVID-19; Coronavirus; J48; MOSHO; deep learning; optimization.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
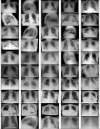
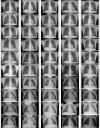
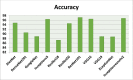
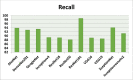
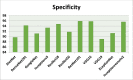
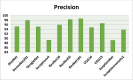
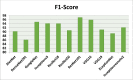


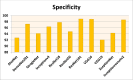
References
-
- Celik, Y., Talo, M., Yildirim, O., Karabatak, M., & Acharya, U. R. (2020). Automated invasive ductal carcinoma detection based using deep transfer learning with whole-slide images. Pattern Recognition Letters, 133, 232–239. 10.1016/j.patrec.2020.03.011 - DOI
-
- Dhiman, G. (2019). ESA: A hybrid bio-inspired metaheuristic optimization approach for engineering problems. Engineering with Computers, 1–31.
-
- Dhiman, G. (2020). MOSHEPO: A hybrid multi-objective approach to solve economic load dispatch and micro grid problems. Applied Intelligence, 50(1), 119–137. 10.1007/s10489-019-01522-4 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
