Islet Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults Taking Sitagliptin: A Randomized Trial
- PMID: 33475138
- PMCID: PMC7993585
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab026
Islet Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults Taking Sitagliptin: A Randomized Trial
Abstract
Context: The long-term effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) are unclear.
Objective: To investigate the effects of sitagliptin on β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in LADA patients receiving insulin.
Design and setting: A randomized controlled trial at the Second Xiangya Hospital.
Methods: Fifty-one patients with LADA were randomized to sitagliptin + insulin (SITA) group or insulin alone (CONT) group for 24 months.
Main outcome measures: Fasting C-peptide (FCP), 2-hour postprandial C-peptide (2hCP) during mixed-meal tolerance test, △CP (2hCP - FCP), and updated homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function (HOMA2-B) were determined every 6 months. In 12 subjects, hyperglycemic clamp and hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp (HEC) tests were further conducted at 12-month intervals.
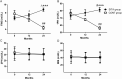
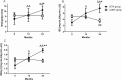
Results: During the 24-month follow-up, there were no significant changes in β-cell function in the SITA group, whereas the levels of 2hCP and △CP in the CONT group were reduced at 24 months. Meanwhile, the changes in HOMA2-B from baseline were larger in the SITA group than in the CONT group. At 24 months, first-phase insulin secretion was improved in the SITA group by hyperglycemia clamp, which was higher than in the CONT group (P < .001), while glucose metabolized (M), insulin sensitivity index, and M over logarithmical insulin ratio in HEC were increased in the SITA group (all P < .01 vs baseline), which were higher than in the CONT group.
Conclusion: Compared with insulin intervention alone, sitagliptin plus insulin treatment appeared to maintain β-cell function and improve insulin sensitivity in LADA to some extent.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01159847.
Keywords: insulin sensitivity; islet β-cell function; latent autoimmune diabetes in adults; sitagliptin.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor From Grill et al: "Islet Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults Taking Sitagliptin: A Randomized Trial".J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Sep 27;106(10):e4296-e4297. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab411. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34114012 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to the Letter to the Editor from Valdemar Grill et al: "Islet Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults Taking Sitagliptin: A Randomized Trial".J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Sep 27;106(10):e4304-e4305. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab413. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34114619 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Altered T-cell subsets and transcription factors in latent autoimmune diabetes in adults taking sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor: A 1-year open-label randomized controlled trial.J Diabetes Investig. 2019 Mar;10(2):375-382. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12873. Epub 2018 Aug 3. J Diabetes Investig. 2019. PMID: 29883070 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor sitagliptin maintains β-cell function in patients with recent-onset latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: one year prospective study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 May;99(5):E876-80. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3633. Epub 2014 Jan 16. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24432999 Clinical Trial.
-
Investigating optimal β-cell-preserving treatment in latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: Results from a 21-month randomized trial.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Oct;21(10):2219-2227. doi: 10.1111/dom.13797. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019. PMID: 31148332 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin and insulin for latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Diabetes Investig. 2022 Sep;13(9):1506-1519. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13814. Epub 2022 May 6. J Diabetes Investig. 2022. PMID: 35445591 Free PMC article.
-
Sitagliptin: Profile of a novel DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Drugs Today (Barc). 2007 Jan;43(1):13-25. doi: 10.1358/dot.2007.43.1.1043909. Drugs Today (Barc). 2007. PMID: 17315049 Review.
Cited by
-
Letter to the Editor From Grill et al: "Islet Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults Taking Sitagliptin: A Randomized Trial".J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Sep 27;106(10):e4296-e4297. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab411. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34114012 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An Adult Case of Diabetes With High Levels of GAD Antibodies Without Insulin Deficiency for More Than 10 Years.Case Rep Endocrinol. 2025 Feb 27;2025:9712659. doi: 10.1155/crie/9712659. eCollection 2025. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40226121 Free PMC article.
-
Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults in China.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 25;13:977413. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.977413. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36090989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Regimens in the Treatment of Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults: A Network Meta-analysis.Diabetes Ther. 2023 Oct;14(10):1723-1752. doi: 10.1007/s13300-023-01459-5. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Diabetes Ther. 2023. PMID: 37584857 Free PMC article.
-
Response to the Letter to the Editor from Valdemar Grill et al: "Islet Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults Taking Sitagliptin: A Randomized Trial".J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Sep 27;106(10):e4304-e4305. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab413. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34114619 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Xiang Y, Huang G, Zhu Y, et al. ; China National D, Metabolic Disorders Study G. Identification of autoimmune type 1 diabetes and multiple organ-specific autoantibodies in adult-onset non-insulin-requiring diabetes in China: a population-based multicentre nationwide survey. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(4):893-902. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi T, Nakanishi K, Murase T, Kosaka K. Small doses of subcutaneous insulin as a strategy for preventing slowly progressive beta-cell failure in islet cell antibody-positive patients with clinical features of NIDDM. Diabetes. 1996;45(5):622-626. - PubMed
-
- Maruyama T, Tanaka S, Shimada A, et al. . Insulin intervention in slowly progressive insulin-dependent (type 1) diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(6):2115-2121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

