Long-term Therapeutic Success of Intravenous Rituximab in 26 Patients with Indolent Primary Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 33475146
- PMCID: PMC9366677
- DOI: 10.2340/00015555-3746
Long-term Therapeutic Success of Intravenous Rituximab in 26 Patients with Indolent Primary Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
Abstract
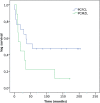
Systemic monotherapy with rituximab is a well-known treatment approach for primary cutaneous follicle centre lymphoma and primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma. Both have excellent prognosis despite high relapse rates. To investigate the long-term effectiveness and clinical outcome of intravenous rituximab at a dose of 375 mg/m2 once weekly, data for 26 patients (17 primary cutaneous follicle centre lymphoma and 9 primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma) were analysed retrospectively. Complete remissions occurred in 20 (77%) and partial remissions in 6 patients (23%), demonstrating an overall response rate of 100%. The relapse rate was 52.9% in primary cutaneous follicle centre lymphoma and 88.9% in primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma. Ongoing complete remissions after therapy with rituximab were observed in 9 patients (34.6%) with a median progression-free survival of 161 months (13.4 years). These results confirm that intravenous rituximab is an effective and well-tolerated treatment with durable responses in a relevant percentage of patients at a median follow-up of 148 months (12.3 years).
Keywords: follow-up; intravenous rituximab therapy; primary cutaneous follicle centre lymphoma; primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma; primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Zinzani PL, Quaglino P, Pimpinelli N, Berti E, Baliva G, Rupoli S, et al. Prognostic factors in primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma: the Italian Study Group for Cutaneous Lymphomas. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 1376–1382. - PubMed
-
- Bogle MA, Riddle CC, Triana EM, Jones D, Duvic M. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 2005; 53: 479–484. - PubMed
-
- Wilcox RA. Cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: 2019 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 2018; 93: 1427–1430. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources