Parkinson-like early autonomic dysfunction induced by vagal application of DOPAL in rats
- PMID: 33475253
- PMCID: PMC8025611
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.13589
Parkinson-like early autonomic dysfunction induced by vagal application of DOPAL in rats
Abstract
Aim: To understand why autonomic failures, a common non-motor symptom of Parkinson's disease (PD), occur earlier than typical motor disorders.
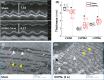
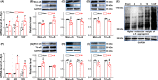
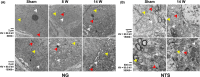
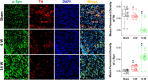
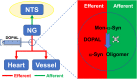
Methods: Vagal application of DOPAL (3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde) to simulate PD-like autonomic dysfunction and understand the connection between PD and cardiovascular dysfunction. Molecular and morphological approaches were employed to test the time-dependent alternation of α-synuclein aggregation and the ultrastructure changes in the heart and nodose (NG)/nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS).
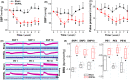
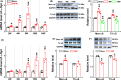
Results: Blood pressure (BP) and baroreflex sensitivity of DOPAL-treated rats were significantly reduced accompanied with a time-dependent change in orthostatic BP, consistent with altered echocardiography and cardiomyocyte mitochondrial ultrastructure. Notably, time-dependent and collaborated changes in Mon-/Tri-α-synuclein were paralleled with morphological alternation in the NG and NTS.
Conclusion: These all demonstrate that early autonomic dysfunction mediated by vagal application of DOPAL highly suggests the plausible etiology of PD initiated from peripheral, rather than central site. It will provide a scientific basis for the prevention and early diagnosis of PD.
Keywords: DOPAL; Parkinson's disease; autonomic dysfunction; vagus; α-synuclein.
© 2021 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest associated with the contents of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Schapira AHV, Chaudhuri KR, Jenner P. Non‐motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18:509. - PubMed
-
- Kuhlenbaumer G, Berg D. Parkinson disease genetics: too early to predict progression? Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15:625‐626. - PubMed
-
- Sartori M, Pessina AC. Orthostatic hypotension and supine hypertension in pure autonomic failure. Ital HeartJ Suppl. 2004;5:879‐882. - PubMed
-
- Espay AJ, LeWitt PA, Hauser RA, et al. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension and supine hypertension in Parkinson's disease and related synucleinopathies: prioritisation of treatment targets. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:954‐966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

