SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase as a therapeutic target for COVID-19
- PMID: 33475441
- PMCID: PMC7938656
- DOI: 10.1080/13543776.2021.1880568
SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase as a therapeutic target for COVID-19
Abstract
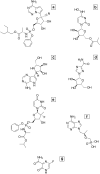
Introduction: The current SARS-CoV-2 pandemic urgently demands for both prevention and treatment strategies. RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (RdRp), which has no counterpart in human cells, is an excellent target for drug development. Given the time-consuming process of drug development, repurposing drugs approved for other indications or at least successfully tested in terms of safety and tolerability, is an attractive strategy to rapidly provide an effective medication for severe COVID-19 cases.Areas covered: The currently available data and upcominSg studies on RdRp which can be repurposed to halt SARS-CoV-2 replication, are reviewed.Expert opinion: Drug repurposing and design of novel compounds are proceeding in parallel to provide a quick response and new specific drugs, respectively. Notably, the proofreading SARS-CoV-2 exonuclease activity could limit the potential for drugs designed as immediate chain terminators and favor the development of compounds acting through delayed termination. While vaccination is awaited to curb the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic, even partially effective drugs from repurposing strategies can be of help to treat severe cases of disease. Considering the high conservation of RdRp among coronaviruses, an improved knowledge of its activity in vitro can provide useful information for drug development or drug repurposing to combat SARS-CoV-2 as well as future pandemics.
Keywords: COVID-19; drug repurposing; nucleoside inhibitors; rna polymerase; sars-CoV-2.
Figures
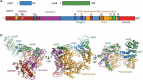
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
