Salmonella effector SpvB aggravates dysregulation of systemic iron metabolism via modulating the hepcidin-ferroportin axis
- PMID: 33475464
- PMCID: PMC7833757
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1849996
Salmonella effector SpvB aggravates dysregulation of systemic iron metabolism via modulating the hepcidin-ferroportin axis
Abstract
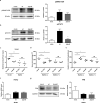
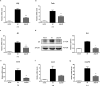
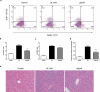
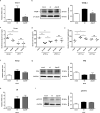
Iron withholding, an essential component of nutritional immunity, plays a fundamental role in host resistance to Salmonella infection. Our previous study showed that SpvB, an important pSLT-encoded cytotoxic effector, facilitated Salmonella pathogenesis within macrophages via perturbing cellular iron metabolism. However, the underlying mechanisms of SpvB in Salmonella-relevant disorders of systemic iron metabolism have not yet been identified. Here, we demonstrated that SpvB facilitated Salmonella to scavenge iron from the host by modulating the hepcidin-ferroportin axis, a key regulator of systemic iron metabolism. We observed that SpvB enhanced hepatic hepcidin synthesis in a STAT3-dependent manner, but not the BMP/SMAD pathway. This subsequently resulted in a reduction of the unique cellular iron exporter ferroportin, which facilitated hypoferremia and hepatic iron accumulation and ultimately countered the limitation of iron availability, thereby improving the chances of Salmonella survival and replication. Moreover, SpvB promoted the production of proinflammatory molecules associated with the infiltration of inflammatory cells via highly upregulating TREM-1 signaling. Our data supported a role of TREM-1 in SpvB-related dysregulation of host iron metabolism and suggested that targeting TREM-1 might provide a potential therapeutic strategy to prevent or alleviate Salmonella pathogenesis.
Keywords: Salmonella; SpvB; systemic iron metabolism; TREM-1; hepcidin–ferroportin axis.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
