Corneal Keratocyte Density and Corneal Nerves Are Reduced in Patients With Severe Obesity and Improve After Bariatric Surgery
- PMID: 33475689
- PMCID: PMC7817877
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.62.1.20
Corneal Keratocyte Density and Corneal Nerves Are Reduced in Patients With Severe Obesity and Improve After Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
Purpose: Obesity is associated with peripheral neuropathy, which bariatric surgery may ameliorate. The aim of this study was to assess whether corneal confocal microscopy can show a change in corneal nerve morphology and keratocyte density in subjects with severe obesity after bariatric surgery.
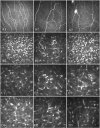
Methods: Twenty obese patients with diabetes (n = 13) and without diabetes (n = 7) underwent assessment of hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), lipids, IL-6, highly sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP), and corneal confocal microscopy before and 12 months after bariatric surgery. Corneal nerve fiber density (CNFD), corneal nerve branch density (CNBD), corneal nerve fiber length (CNFL), and keratocyte density (KD) from the anterior, middle, and posterior stroma were quantified. Twenty-two controls underwent assessment at baseline only.
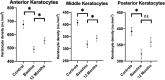
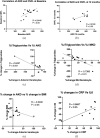
Results: CNFL (P < 0.001), CNBD (P < 0.05), and anterior (P < 0.001), middle (P < 0.001), and posterior (P < 0.001) keratocyte densities were significantly lower in obese patients compared to controls, and anterior keratocyte density (AKD) correlated with CNFL. Twelve months after bariatric surgery, there were significant improvements in body mass index (BMI; P < 0.001), HDL cholesterol (P < 0.05), hsCRP (P < 0.001), and IL-6 (P < 0.01). There were significant increases in CNFD (P < 0.05), CNBD (P < 0.05), CNFL (P < 0.05), and anterior (P < 0.05) and middle (P < 0.001) keratocyte densities. The increase in AKD correlated with a decrease in BMI (r = -0.55, P < 0.05) and triglycerides (r = -0.85, P < 0.001). There were no significant correlations between the change in keratocyte densities and corneal nerve fiber or other neuropathy measures.
Conclusions: Corneal confocal microscopy demonstrates early small fiber damage and reduced keratocyte density in obese patients. Bariatric surgery leads to weight reduction and improvement in lipids and inflammation and an improvement in keratocyte density and corneal nerve regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

Similar articles
-
Keratocyte Density Is Reduced and Related to Corneal Nerve Damage in Diabetic Neuropathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Jul 2;59(8):3584-3590. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-23889. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30025082
-
No Relation Between the Severity of Corneal Nerve, Epithelial, and Keratocyte Cell Morphology With Measures of Dry Eye Disease in Type 1 Diabetes.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Nov 1;59(13):5525-5530. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-25321. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30480740
-
Small Nerve Fiber Damage and Langerhans Cells in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes and LADA Measured by Corneal Confocal Microscopy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 May 3;62(6):5. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.6.5. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33944892 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo confocal microscopy of corneal nerves: analysis and clinical correlation.Semin Ophthalmol. 2010 Sep-Nov;25(5-6):171-7. doi: 10.3109/08820538.2010.518133. Semin Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 21090996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corneal in vivo Confocal Microscopy for Assessment of Non-Neurological Autoimmune Diseases: A Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 9;9:809164. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.809164. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35372389 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Obesity negatively impacts corneal nerves in patients with diabetes mellitus.Eye Vis (Lond). 2025 Apr 23;12(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40662-025-00433-5. Eye Vis (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40270066 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo corneal confocal microscopy as a non-invasive test to assess obesity induced small fibre nerve damage and inflammation.Eye (Lond). 2023 Aug;37(11):2226-2232. doi: 10.1038/s41433-022-02321-x. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Eye (Lond). 2023. PMID: 36443498 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathy 10-15 years after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for severe obesity: A community-controlled nerve conduction study.Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2024 Mar 27;9:130-137. doi: 10.1016/j.cnp.2024.03.002. eCollection 2024. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2024. PMID: 38618240 Free PMC article.
-
The Peripheral Neuropathy Prevalence and Characteristics Are Comparable in People with Obesity and Long-Duration Type 1 Diabetes.Adv Ther. 2022 Sep;39(9):4218-4229. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02208-z. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35867275 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Effect of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference on Ocular Health Parameters in Children and Adolescents.Children (Basel). 2025 Mar 26;12(4):413. doi: 10.3390/children12040413. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40310070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam S, Liu Y, Siahmansur T, et al. .. Bariatric surgery as a model to explore the basis and consequences of the Reaven hypothesis: small, dense low-density lipoprotein and interleukin-6. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2019; 16(2): 144–152. - PubMed
-
- Herman RM, Brower JB, Stoddard DG, et al. .. Prevalence of somatic small fiber neuropathy in obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 2007; 31(2): 226–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

