Short Wavelength (Blue) Light Is Protective for Lens-Induced Myopia in Guinea Pigs Potentially Through a Retinoic Acid-Related Mechanism
- PMID: 33475690
- PMCID: PMC7817876
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.62.1.21
Short Wavelength (Blue) Light Is Protective for Lens-Induced Myopia in Guinea Pigs Potentially Through a Retinoic Acid-Related Mechanism
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the effect of short-wavelength light (SL) on guinea pigs with lens-induced myopia (LIM) and the possible retinoic acid (RA)-related mechanisms.
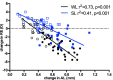
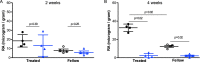
Methods: Two-week-old guinea pigs (n = 60) with monocular -5D lenses were reared under white light (WL, 580 lux) or SL (440 nm, 500 lux). The left eyes were uncovered as control. Refractive error (RE) and axial length (AL) were measured at baseline, one week, two weeks, and four weeks after intervention. Retinal RA was measured from four guinea pigs after two and four weeks of treatment with HPLC. Two-week-old guinea pigs (n = 52) with monocular -5D lens were fed with either RA or its synthesis inhibitor citral every third day in the morning, and half from each group were reared under WL or SL conditions. RE and AL were recorded at baseline and two and four weeks after intervention. Retinal RA was measured after four weeks of intervention.
Results: At the end of treatment, guinea pigs exposed to SL were less myopic than to WL (2.06 ± 1.69D vs. -1.00 ± 1.88D), accompanied with shorter AL (P = 0.01) and less retinal RA (P = 0.02). SL reduced retinal RA even after exogenous RA supplementation (P = 0.02) and decelerated LIM compared to WL (1.66 ± 1.03D vs. -3.53 ± 0.90D). Citral slowed ocular growth, leading to similar RE in W+CI and S+CI groups (3.39 ± 1.65D vs. 5.25 ± 0.80D).
Conclusions: Overall, SL reduced LIM in guinea pigs, even in those supplemented with oral RA, accompanied by reduced retinal RA levels. Oral RA accelerated eye elongation, but citral equally decelerated eye elongation under SL and WL with no significant retinal RA reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures




Similar articles
-
Myopia induced by flickering light in guinea pig eyes is associated with increased rather than decreased dopamine release.Mol Vis. 2017 Sep 29;23:666-679. eCollection 2017. Mol Vis. 2017. PMID: 28966549 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Expression of GJD2 Messenger RNA and the Coded Protein Connexin 36 in Negative Lens-induced Myopia of Guinea Pigs.Optom Vis Sci. 2020 Dec;97(12):1080-1088. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001611. Optom Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 33278187 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Retinal Melanopsin on Lens-induced Myopia in Guinea Pigs.Optom Vis Sci. 2020 Jul;97(7):489-495. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001529. Optom Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32697555
-
An updated view on the role of dopamine in myopia.Exp Eye Res. 2013 Sep;114:106-19. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.02.007. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23434455 Review.
-
What Do Animal Studies Tell Us about the Mechanism of Myopia-Protection by Light?Optom Vis Sci. 2016 Sep;93(9):1049-51. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000917. Optom Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27362614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Light and myopia: from epidemiological studies to neurobiological mechanisms.Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2021 Dec 19;13:25158414211059246. doi: 10.1177/25158414211059246. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34988370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal bright light at low frequency retards lens-induced myopia in guinea pigs.PeerJ. 2023 Nov 14;11:e16425. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16425. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38025747 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Exposure to Blue Light Shows an Inhibitory Effect on Axial Elongation in Human Eyes Independent of Defocus.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Dec 1;62(15):22. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.15.22. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34935883 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Transcriptome and Proteome Analyses Elucidate the Mechanism of Lens-Induced Myopia in Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Oct 3;64(13):15. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.13.15. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37819745 Free PMC article.
-
The Changes of KCNQ5 Expression and Potassium Microenvironment in the Retina of Myopic Guinea Pigs.Front Physiol. 2021 Dec 23;12:790580. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.790580. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 35002772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hung LF, Crawford MLJ, Smith EL.. Spectacle lenses alter eye growth and the refractive status of young monkeys. Nat Med. 1995; 1(8): 761–765. - PubMed
-
- Graham B, Judge SJ.. The effects of spectacle wear in infancy on eye growth and refractive error in the marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Vision Res. 1999; 39(2): 189–206. - PubMed
-
- Whatham AR, Judge SJ.. Compensatory changes in eye growth and refraction induced by daily wear of soft contact lenses in young marmosets. Vision Res. 2001; 41(3): 267–273. - PubMed
-
- Mcfadden SA, Howlett MHC, Mertz JR.. Retinoic acid signals the direction of ocular elongation in the guinea pig eye. Vision Res. 2004; 44: 643–653. - PubMed
-
- Howlett MHC, McFadden SA.. Spectacle lens compensation in the pigmented guinea pig. Vision Res. 2009; 49(2): 219–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

