Discovery and function exploration of microRNA-155 as a molecular biomarker for early detection of breast cancer
- PMID: 33475963
- PMCID: PMC8213678
- DOI: 10.1007/s12282-021-01215-2
Discovery and function exploration of microRNA-155 as a molecular biomarker for early detection of breast cancer
Abstract
Background: MicroRNA-155 (miR-155) may function as a diagnostic biomarker of breast cancer (BC). Nevertheless, the available evidence is controversial. Therefore, we performed this study to summarize the global predicting role of miR-155 for early detection of BC and preliminarily explore the functional roles of miR-155 in BC.
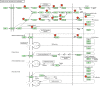
Methods: We first collected published studies and applied the bivariate meta-analysis model to generate the pooled diagnostic parameters of miR-155 in diagnosing BC such as sensitivity, specificity and area under curve (AUC). Then, we applied function enrichment and protein-protein interactions (PPI) analyses to explore the potential mechanisms of miR-155.
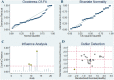
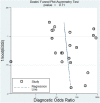
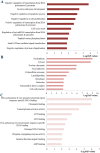
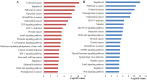
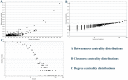
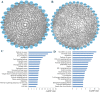
Results: A total of 21 studies were finally included. The results indicated that miR-155 allowed for the discrimination between BC patients and healthy controls with a sensitivity of 0.87 (95% CI 0.78-0.93), specificity of 0.82 (0.72-0.89), and AUC of 0.91 (0.88-0.93). In addition, the overall sensitivity, specificity and AUC for circulating miR-155 were 0.88 (0.76-0.95), 0.83 (0.72-0.90), and 0.92 (0.89-0.94), respectively. Function enrichment analysis revealed several vital ontologies terms and pathways associated with BC occurrence and development. Furthermore, in the PPI network, ten hub genes and two significant modules were identified to be involved in some important pathways associated with the pathogenesis of BC.
Conclusions: We demonstrated that miR-155 has great potential to facilitate accurate BC detection and may serve as a promising diagnostic biomarker for BC. However, well-designed cohort studies and biological experiments should be implemented to confirm the diagnostic value of miR-155 before it can be applied to routine clinical procedures.
Keywords: Biomarker; Breast cancer; Diagnosis; MicroRNA-155.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of upregulated miR-375 expression in breast cancer: An in vitro and in silico study.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Jan;216(1):152754. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152754. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 31787478
-
Combined detection of plasma miR-127-3p and HE4 improves the diagnostic efficacy of breast cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2017;18(2):143-148. doi: 10.3233/CBM-160024. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 27983524
-
A Signature of Four Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosing Early-Stage Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 6;22(11):6121. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116121. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34204158 Free PMC article.
-
Appraising MicroRNA-155 as a Noninvasive Diagnostic Biomarker for Cancer Detection: A Meta-Analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jan;95(2):e2450. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002450. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 26765436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of MiR-155 in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 14;21(16):5834. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165834. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32823863 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic and diagnostic values of non-coding RNAs as biomarkers for breast cancer: An umbrella review and pan-cancer analysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jan 16;10:1096524. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1096524. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36726376 Free PMC article.
-
Potential utility of miRNAs for liquid biopsy in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 4;12:940314. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.940314. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35992785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs in Cancer (Review of Literature).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 3;23(5):2805. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052805. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of three miRNA signature as potential diagnostic marker for triple negative breast cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 8;13(1):21643. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48896-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38062163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Ma J, Gaudet MM, Newman LA, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Jemal A, Siegel RL. Breast cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(6):438–451. - PubMed
-
- Schunemann HJ, Lerda D, Quinn C, Follmann M, Alonso-Coello P, Rossi PG, Lebeau A, Nystrom L, Broeders M, Ioannidou-Mouzaka L, Duffy SW, Borisch B, Fitzpatrick P, Hofvind S, Castells X, Giordano L, Canelo-Aybar C, Warman S, Mansel R, Sardanelli F, Parmelli E, Grawingholt A, Saz-Parkinson Z, European Commission Initiative on Breast Cancer Contributor G Breast cancer screening and diagnosis: a synopsis of the European breast guidelines. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(1):46–56. - PubMed
-
- Treiber T, Treiber N, Meister G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other cellular pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1):5–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

