Evaluation of Abbott BinaxNOW Rapid Antigen Test for SARS-CoV-2 Infection at Two Community-Based Testing Sites - Pima County, Arizona, November 3-17, 2020
- PMID: 33476316
- PMCID: PMC7821766
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7003e3
Evaluation of Abbott BinaxNOW Rapid Antigen Test for SARS-CoV-2 Infection at Two Community-Based Testing Sites - Pima County, Arizona, November 3-17, 2020
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Vol. 70, No. 3.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021 Jan 29;70(4):144. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7004a6. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021. PMID: 33507886 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
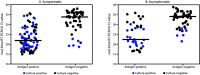
Rapid antigen tests, such as the Abbott BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag Card (BinaxNOW), offer results more rapidly (approximately 15-30 minutes) and at a lower cost than do highly sensitive nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) (1). Rapid antigen tests have received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for use in symptomatic persons (2), but data are lacking on test performance in asymptomatic persons to inform expanded screening testing to rapidly identify and isolate infected persons (3). To evaluate the performance of the BinaxNOW rapid antigen test, it was used along with real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing to analyze 3,419 paired specimens collected from persons aged ≥10 years at two community testing sites in Pima County, Arizona, during November 3-17, 2020. Viral culture was performed on 274 of 303 residual real-time RT-PCR specimens with positive results by either test (29 were not available for culture). Compared with real-time RT-PCR testing, the BinaxNOW antigen test had a sensitivity of 64.2% for specimens from symptomatic persons and 35.8% for specimens from asymptomatic persons, with near 100% specificity in specimens from both groups. Virus was cultured from 96 of 274 (35.0%) specimens, including 85 (57.8%) of 147 with concordant antigen and real-time RT-PCR positive results, 11 (8.9%) of 124 with false-negative antigen test results, and none of three with false-positive antigen test results. Among specimens positive for viral culture, sensitivity was 92.6% for symptomatic and 78.6% for asymptomatic individuals. When the pretest probability for receiving positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 is elevated (e.g., in symptomatic persons or in persons with a known COVID-19 exposure), a negative antigen test result should be confirmed by NAAT (1). Despite a lower sensitivity to detect infection, rapid antigen tests can be an important tool for screening because of their quick turnaround time, lower costs and resource needs, high specificity, and high positive predictive value (PPV) in settings of high pretest probability. The faster turnaround time of the antigen test can help limit transmission by more rapidly identifying infectious persons for isolation, particularly when used as a component of serial testing strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- CDC. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): interim guidance for rapid antigen testing for SARS-CoV-2. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antigen-tests-gu...
-
- Food and Drug Administration. In vitro diagnostics EUAs. Silver Spring, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration; 2020. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-em...
-
- CDC. COVID-19: CDC guidance for expanded screening testing to reduce silent spread of SARS-CoV-2. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/php/open-america/expanded-scre...
-
- Abbott. BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag card (PN 195–000)—instructions for use. Abbott Park, IL: Abbott; 2020. https://www.fda.gov/media/141570/download
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

