Acute Immune Signatures and Their Legacies in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Infected Cancer Patients
- PMID: 33476581
- PMCID: PMC7833668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.01.001
Acute Immune Signatures and Their Legacies in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Infected Cancer Patients
Abstract
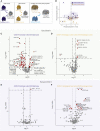
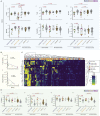
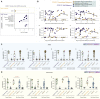
Given the immune system's importance for cancer surveillance and treatment, we have investigated how it may be affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection of cancer patients. Across some heterogeneity in tumor type, stage, and treatment, virus-exposed solid cancer patients display a dominant impact of SARS-CoV-2, apparent from the resemblance of their immune signatures to those for COVID-19+ non-cancer patients. This is not the case for hematological malignancies, with virus-exposed patients collectively displaying heterogeneous humoral responses, an exhausted T cell phenotype and a high prevalence of prolonged virus shedding. Furthermore, while recovered solid cancer patients' immunophenotypes resemble those of non-virus-exposed cancer patients, recovered hematological cancer patients display distinct, lingering immunological legacies. Thus, while solid cancer patients, including those with advanced disease, seem no more at risk of SARS-CoV-2-associated immune dysregulation than the general population, hematological cancer patients show complex immunological consequences of SARS-CoV-2 exposure that might usefully inform their care.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; cancer; hemato-oncological; immune; seroconversion; vaccine; virus shedding.
Crown Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Cooper N., Arnold D.M. The effect of rituximab on humoral and cell mediated immunity and infection in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Br. J. Haematol. 2010;149:3–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

