Prophylaxis for COVID-19: a systematic review
- PMID: 33476807
- PMCID: PMC7813508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.013
Prophylaxis for COVID-19: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: While the landscape of vaccine and treatment candidates against the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been reviewed systematically, prophylactic candidates remain unexplored.
Objectives: To map pre- and postexposure prophylactic (PrEP and PEP) candidate for COVID-19.
Data sources: PubMed/Medline, Embase, International Committee of Medical Journal Editors and International Clinical Trials Registry Platform clinical trial registries and medRxiv.
Study eligibility criteria and participants: All studies in humans or animals and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in humans reporting primary data on prophylactic candidates against COVID-19, excluding studies focused on key populations.
Interventions: PrEP and PEP candidate for COVID-19.
Methods: Systematic review and qualitative synthesis of COVID-19 PrEP and PEP studies and RCTs complemented by search of medRxiv and PubMed and Embase for studies reporting RCT outcomes since systematic review search completion.
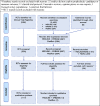
Results: We identified 13 studies (from 2119 database records) and 117 RCTs (from 5565 RCTs listed in the registries) that met the inclusion criteria. Non-RCT studies reported on cross-sectional studies using hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in humans (n = 2) or reported on animal studies (n = 7), most of which used antibodies. All five completed RCTs focused on the use of HCQ as either PrEP or PEP, and these and the cross-sectional studies reported no prophylactic effect. The majority of ongoing RCTs evaluated HCQ or other existing candidates including non-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccines, anti(retro)virals or use of vitamins and supplements.
Conclusions: The key message from completed studies and RCTs seems to be that HCQ does not work. There is little evidence regarding other compounds, with all RCTs using candidates other than HCQ still ongoing. It remains to be seen if the portfolio of existing molecules being evaluated in RCTs will identify successful prophylaxis against COVID-19 or if there is a need for the development of new candidates.
Keywords: COVID-19; Prophylaxis; Randomized control trials; SARS-CoV-2; Systematic review.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine for prevention and treatment of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 12;2(2):CD013587. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013587.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33624299 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of hydroxychloroquine for post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection among adults exposed to coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jun 3;21(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04446-4. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32493478 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-exposure prophylaxis with hydroxychloroquine for high-risk healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: A structured summary of a study protocol for a multicentre, double-blind randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jul 29;21(1):688. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04621-7. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32727613 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine as pre-and post-exposure prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trials.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2021 Oct;2:100062. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2021.100062. Epub 2021 Aug 29. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2021. PMID: 34485970 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A study protocol for a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of carrageenan nasal and throat spray for COVID-19 prophylaxis-ICE-COVID.Trials. 2022 Sep 15;23(1):782. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06685-z. Trials. 2022. PMID: 36109791 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposed drug studies on the primary prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection during the pandemic: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023 Aug;10(1):e001674. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2023-001674. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37640510 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular design of a pathogen activated, self-assembling mechanopharmaceutical device.J Control Release. 2022 Jul;347:620-631. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.029. Epub 2022 May 28. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35623493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review.Lupus. 2022 May;31(6):684-696. doi: 10.1177/09612033221093502. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Lupus. 2022. PMID: 35382637 Free PMC article.
-
Maoto, a traditional herbal medicine, for post-exposure prophylaxis for Japanese healthcare workers exposed to COVID-19: A single center study.J Infect Chemother. 2022 Jul;28(7):907-911. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2022.03.014. Epub 2022 Mar 21. J Infect Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35361537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vaughan A. 16 September 2020. Coronavirus death toll reaches 1 million – how did we get here? New Scientist.https://www.newscientist.com/article/mg24733003-600-coronavirus-death-to... Available at:
-
- European Data Portal . 30 June 2020. Pressure on healthcare systems: coping with demand for ICU and hospital beds.https://www.europeandataportal.eu/en/impact-studies/covid-19/pressure-he... Available at:
-
- World Bank . 8 June 2020. The global economic outlook during the COVID-19 pandemic: a changed world.https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2020/06/08/the-global-economic... Available at:
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

