Human neutrophil membrane-derived nanovesicles as a drug delivery platform for improved therapy of infectious diseases
- PMID: 33476827
- PMCID: PMC7920994
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.01.020
Human neutrophil membrane-derived nanovesicles as a drug delivery platform for improved therapy of infectious diseases
Abstract
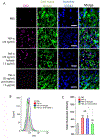
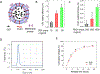
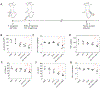
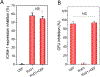
Resolvins are a group of specialized proresolving lipid mediators (SPMs) enzymatically produced from omega-3 fatty acids during acute inflammation response to infections or tissue injury. Resolvin D1 (RvD1) is one of resolvins and is well studied in resolution of inflammation to treat inflammatory diseases. Resolution of inflammation includes the inhibition of polymorphonuclear leukocyte recruitment and reduced cytokine production. However, effective delivery of RvD1 to inflammatory tissues is challenging because of its lack of tissue targeting and poor physicochemical properties. Here, we proposed nanovesicles made from human neutrophil membrane which can specifically target inflamed tissues, and we loaded RvD1 on the surface of nanovesicles and antibiotic (ceftazidime, CEF) inside nanovesicles for improved treatment of bacterial infections. In a mouse model of bacterium-induced peritonitis, we demonstrated that human neutrophil cell membrane-formed vesicles (NMVs) enhanced inflammation resolution and bacterial killing after co-delivery of RvD1 and CEF. Our studies reveal that neutrophil nanovesicles may be critical for enhanced therapy to infectious diseases.
Keywords: Ceftazidime; Neutrophil-membrane formed vesicles; Peritonitis; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Resolvin D1.
Copyright © 2021 Acta Materialia Inc. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None of the authors have any possible conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Co-delivery of resolvin D1 and antibiotics with nanovesicles to lungs resolves inflammation and clears bacteria in mice.Commun Biol. 2020 Nov 16;3(1):680. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01410-5. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 33199819 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Dynamics Simulations Provide Insight into the Loading Efficiency of Proresolving Lipid Mediators Resolvin D1 and D2 in Cell Membrane-Derived Nanovesicles.Mol Pharm. 2020 Jun 1;17(6):2155-2164. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00299. Epub 2020 May 19. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32374613 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoresolving actions of oral resolvin D1 include selective regulation of the transcription machinery in resolution-phase mouse macrophages.FASEB J. 2014 Jul;28(7):3090-102. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-248393. Epub 2014 Apr 1. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24692596
-
Neutrophil-Based Drug Delivery Systems.Adv Mater. 2018 May;30(22):e1706245. doi: 10.1002/adma.201706245. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 29577477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolvins, specialized proresolving lipid mediators, and their potential roles in metabolic diseases.Cell Metab. 2014 Jan 7;19(1):21-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.10.006. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Cell Metab. 2014. PMID: 24239568 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil-inspired photothermo-responsive drug delivery system for targeted treatment of bacterial infection and endotoxins neutralization.Biomater Res. 2023 Apr 15;27(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40824-023-00372-z. Biomater Res. 2023. PMID: 37061741 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering bacterial membrane nanovesicles for improved therapies in infectious diseases and cancer.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Jul;186:114340. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114340. Epub 2022 May 13. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35569561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biofunctional lipid nanoparticles for precision treatment and prophylaxis of bacterial infections.Sci Adv. 2024 Apr 5;10(14):eadk9754. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk9754. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38578994 Free PMC article.
-
Application of targeted drug delivery by cell membrane-based biomimetic nanoparticles for inflammatory diseases and cancers.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Oct 30;29(1):523. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02124-8. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39472940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil Membrane Nanovesicles Alleviate the Renal Function Indicators in Acute Kidney Injury Caused by Septic Rats.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun;83(2):2553-2565. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01664-4. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39808397
References
-
- Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P, Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation, Nat Rev Immunol 13(3) (2013) 159–75. - PubMed
-
- Brown KA, Brain SD, Pearson JD, Edgeworth JD, Lewis SM, Treacher DF, Neutrophils in development of multiple organ failure in sepsis, Lancet 368(9530) (2006) 157–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

