Modulation of Insulin Sensitivity by Insulin-Degrading Enzyme
- PMID: 33477364
- PMCID: PMC7830943
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9010086
Modulation of Insulin Sensitivity by Insulin-Degrading Enzyme
Abstract
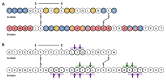
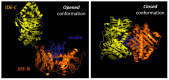
Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) is a highly conserved and ubiquitously expressed metalloprotease that degrades insulin and several other intermediate-size peptides. For many decades, IDE had been assumed to be involved primarily in hepatic insulin clearance, a key process that regulates availability of circulating insulin levels for peripheral tissues. Emerging evidence, however, suggests that IDE has several other important physiological functions relevant to glucose and insulin homeostasis, including the regulation of insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells. Investigation of mice with tissue-specific genetic deletion of Ide in the liver and pancreatic β-cells (L-IDE-KO and B-IDE-KO mice, respectively) has revealed additional roles for IDE in the regulation of hepatic insulin action and sensitivity. In this review, we discuss current knowledge about IDE's function as a regulator of insulin secretion and hepatic insulin sensitivity, both evaluating the classical view of IDE as an insulin protease and also exploring evidence for several non-proteolytic functions. Insulin proteostasis and insulin sensitivity have both been highlighted as targets controlling blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes, so a clearer understanding the physiological functions of IDE in pancreas and liver could led to the development of novel therapeutics for the treatment of this disease.
Keywords: glucose transporters; insulin receptor; insulin resistance; insulin-degrading enzyme; liver; pancreas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- LCF/PR/PR18/51130007/La Caixa" Foundation
- R01 GM115617/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- ORDER EDU/574/2018/Junta de Castilla y León
- GM115617/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- PID2019-110496RB-C21/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- PID2019-110496RB-C22/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- ORDER EDU/556/2019/Junta de Castilla y León
- SAF2016-77871-C2-1-R/Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad
- SAF2016-77871-C2-2-R/Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad
- European Diabetes Research Programme on New Targets for Type 2 Diabetes supported by MSD-2017/European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

