Translational Research in Retinopathy of Prematurity: From Bedside to Bench and Back Again
- PMID: 33477419
- PMCID: PMC7830975
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10020331
Translational Research in Retinopathy of Prematurity: From Bedside to Bench and Back Again
Abstract
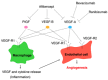
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), a vascular proliferative disease affecting preterm infants, is a leading cause of childhood blindness. Various studies have investigated the pathogenesis of ROP. Clinical experience indicates that oxygen levels are strongly correlated with ROP development, which led to the development of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) as an animal model of ROP. OIR has been used extensively to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying ROP and to evaluate the efficacy of new drug candidates. Large clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents to treat ROP, and anti-VEGF therapy is presently becoming the first-line treatment worldwide. Anti-VEGF therapy has advantages over conventional treatments, including being minimally invasive with a low risk of refractive error. However, long-term safety concerns and the risk of late recurrence limit this treatment. There is an unmet medical need for novel ROP therapies, which need to be addressed by safe and minimally invasive therapies. The recent progress in biotechnology has contributed greatly to translational research. In this review, we outline how basic ROP research has evolved with clinical experience and the subsequent emergence of new drugs. We discuss previous and ongoing trials and present the candidate molecules expected to become novel targets.
Keywords: clinical trial; oxygen-induced retinopathy; retinopathy of prematurity; translational research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Stoll B.J., Hansen N.I., Bell E.F., Walsh M.C., Carlo W.A., Shankaran S., Laptook A.R., Sánchez P.J., Van Meurs K.P., Wyckoff M.H., et al. Trends in Care Practices, Morbidity, and Mortality of Extremely Preterm Neonates, 1993–2012. JAMA. 2015;314:1039–1051. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.10244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

