Fast and Sensitive Screening of Oxandrolone and Its Major Metabolite 17-Epi-Oxandrolone in Human Urine by UHPLC-MS/MS with On-Line SPE Sample Pretreatment
- PMID: 33477515
- PMCID: PMC7831107
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26020480
Fast and Sensitive Screening of Oxandrolone and Its Major Metabolite 17-Epi-Oxandrolone in Human Urine by UHPLC-MS/MS with On-Line SPE Sample Pretreatment
Abstract
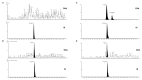
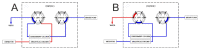
Oxandrolone, a synthetic testosterone analog, is used for the treatment of several diseases associated with weight loss. Unfortunately, oxandrolone is abused by many athletes and bodybuilders due to its strong anabolic effect. We have developed and validated a highly sensitive and rapid on-line SPE-UHPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of oxandrolone and simultaneous identification of its major metabolite 17-epi-oxandrolone in urine matrices. Enrichment of the analytes via an integrated solid-phase extraction was achieved using an Acquity UPLC BEH C18 Column. Subsequently, the chromatographic separation of the on-line preconcentrated sample fraction was achieved using an Acquity HSS T3 C18 Column. For the structural identification of these analytes, a high-resolution mass spectrometer Synapt-G2Si coupled to the Acquity M-class nano-LC system with ionKey source was used. A highly sensitive determination of oxandrolone was achieved using a tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer XEVO TQD. The method was successfully validated in the linear range of oxandrolone from 81.63 pg·mL-1 (limit of quantification, LOQ) to 5000 pg·mL-1 in the human urine matrix. It was applied to the analysis of real urine samples obtained from a healthy volunteer after the oral administration of one dose (10 mg) of oxandrolone. Concentration vs. time dependence was tested in the time interval of 4 h-12 days (after oral administration) to demonstrate the ability of the method to detect the renal elimination of oxandrolone from the human body. Favorable performance parameters along with successful application indicate the usefulness of the proposed method for its routine use in antidoping control labs.
Keywords: 17-epi-oxandrolone; human urine; on-line SPE extraction; oxandrolone; tandem mass spectrometry; ultra-high performance liquid chromatography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A broad-spectrum equine urine screening method for free and enzyme-hydrolysed conjugated drugs with ultra performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Chim Acta. 2011 Jul 4;697(1-2):48-60. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.04.030. Epub 2011 Apr 23. Anal Chim Acta. 2011. PMID: 21641418
-
Rapid screening of anabolic steroids in horse urine with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry after chemical derivatisation.J Chromatogr A. 2012 Apr 6;1232:257-65. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.12.095. Epub 2012 Jan 10. J Chromatogr A. 2012. PMID: 22265177
-
[Determination of trace α-amanitin in urine of mushroom poisoning patient by online solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2020 Nov 8;38(11):1281-1287. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.03010. Se Pu. 2020. PMID: 34213098 Chinese.
-
Ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry determination and profiling of prohibited steroids in human biological matrices. A review.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 May 15;927:22-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 20. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23317577 Review.
-
A targeted UHPLC-MS/MS method to monitor lipidomic changes during a physical effort: Optimization and application to blood microsamples from athletes.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023 May 30;229:115373. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115373. Epub 2023 Mar 28. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023. PMID: 37003087 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultra-sensitive Quantification of Mid-regional Proadrenomedullin in Human Plasma Using Micro-liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry.ACS Omega. 2025 Jun 5;10(23):24214-24223. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c11248. eCollection 2025 Jun 17. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40547652 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and Sensitive Quantification of AccQ-Tag Derivatized Amino Acids and Biogenic Amines by UHPLC-UV Analysis from Complex Biological Samples.Metabolites. 2022 Mar 21;12(3):272. doi: 10.3390/metabo12030272. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35323715 Free PMC article.
-
Safety Implications of Off-Label Medication Use in Athletes: A Narrative Review.Medicines (Basel). 2024 Nov 15;11(8):20. doi: 10.3390/medicines11080020. Medicines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39584970 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pappo R., Jung C.J. 2-oxasteroids: A new class of biologically active compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 1962;3:365–371. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)70883-5. - DOI
-
- Mendenhall C.L., Moritz T.E., Roselle G.A., Morgan T.R., Nemchausky B.A., Tamburro C.H., Schiff E.R., McClain C.J., Marsano L.S., Allen J.I., et al. The VA Cooperative Study Group #275. Protein energy malnutrition in severe alcoholic hepatitis: Diagnosis and response to treatment. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1995;19:258–265. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

