Morphology and Distribution of Antennal Sensilla in Three Species of Thripidae (Thysanoptera) Infesting Alfalfa Medicago sativa
- PMID: 33477621
- PMCID: PMC7831480
- DOI: 10.3390/insects12010081
Morphology and Distribution of Antennal Sensilla in Three Species of Thripidae (Thysanoptera) Infesting Alfalfa Medicago sativa
Abstract
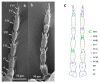
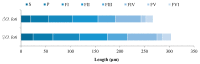
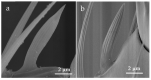
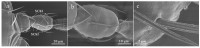
Thrips are important pests to alfalfa Medicago sativa. Similar as many other plant-feeding insects, thrips rely on the antennae to receive chemical signals in the environment to locate their hosts. Previous studies indicated that sensilla of different shapes on the surface of insect antenna play an important role in signal recognition. However, morphological analysis of the antennal sensilla in Thysanoptera has been limited to only a few species. To expand the understanding of how antennal sensilla are related to semiochemical detection in thrips, here we compared the morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla in three thrip species, Odontothrips loti, Megalurothrips distalis, and Sericothrips kaszabi, by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The antennae of these three species are all composed of eight segments and share similar types of sensilla which distribute similarly in each segment, despite that their numbers show sexual dimorphism. Specifically, nine major types of sensilla in total were found, including three types of sensilla basiconica (SBI, SBII, and SBIII), two types of sensilla chaetica (SChI and SChII), and one type for each of sensilla coeloconica (SCo), sensilla trichodea (ST), sensilla campaniformia (SCa), and sensilla cavity (SCav). The potential functions of sensilla were discussed according to the previous research results and will lay a morphological foundation for the study of the olfactory mechanism of three species of thrips.
Keywords: SEM; antennae; sensilla; thrips.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Morphology and Distribution of the Antennal Sensilla of Two Species, Megalurothrips usitatus and Thrips palmi (Thysanoptera: Thripidae).Insects. 2019 Aug 15;10(8):251. doi: 10.3390/insects10080251. Insects. 2019. PMID: 31443161 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling thrips morphology: A comparative analysis of microscopy-based ultrastructural, morphological, and molecular characterization of Thrips tabaci and Thrips parvispinus in onion.Microsc Res Tech. 2024 Dec;87(12):3003-3015. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24653. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Microsc Res Tech. 2024. PMID: 39118418
-
Ultrastructure and distribution of antennal sensilla of the chilli thrips Scirtothrips dorsalis hood (Thysanoptera: Thripidae).Microsc Res Tech. 2017 Dec;80(12):1283-1296. doi: 10.1002/jemt.22926. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Microsc Res Tech. 2017. PMID: 28833941
-
Microscopic morphology and distribution of the antennal sensilla in the double-spined bark beetle, Ips duplicatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae).Microsc Res Tech. 2023 Dec;86(12):1610-1625. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24397. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Microsc Res Tech. 2023. PMID: 37572001
-
Morphology and Distribution of Antennal Sensilla in an Egg Parasitoid Wasp, Anastatus disparis (Hymenoptera: Eupelmidae).J Insect Sci. 2022 Nov 1;22(6):6. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/ieac072. J Insect Sci. 2022. PMID: 36469364 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antennal Transcriptome Analysis of Olfactory Genes and Characterization of Odorant Binding Proteins in Odontothrips loti (Thysanoptera: Thripidae).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 9;24(6):5284. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065284. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982358 Free PMC article.
-
The Plant Volatile-Sensing Mechanism of Insects and Its Utilization.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;13(2):185. doi: 10.3390/plants13020185. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome-level genome assembly of Odontothrips loti Haliday (Thysanoptera: Thripidae).Sci Data. 2024 May 4;11(1):451. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03289-x. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38704405 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission from seed to seedling and elimination of alfalfa viruses.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jun 6;15:1330219. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1330219. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38903432 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence, Distribution, and Transmission of Alfalfa Viruses in China.Viruses. 2022 Jul 12;14(7):1519. doi: 10.3390/v14071519. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35891498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mirab-Balou M., Miri B. Survey of relative frequency and biodiversity indicators changes of thrips species (Insecta: Thysanoptera) in different alfalfa cuttings in Eyvan city (Ilam province) J. Plant Prot. 2019;33:423–430.
-
- Andus L., Trdan S. Thrips species on alfalfa. Biljni Lekar. 2005;33:541–542.
-
- Stuart R.R., Gao Y., Lei Z. Thrips: Pests of concern to China and the United States. Agric. Sci. China. 2011;10:867–892. doi: 10.1016/S1671-2927(11)60073-4. - DOI
-
- Bayar K. Thysanoptera species occurring in the flowers of alfalfa; Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Thysanoptera; Antalya, Turkey. 27 April–1 May 1999; pp. 63–67.
-
- Zhang R., Yang F., Xian C.Z., Ma J.H., Zhang S.H. A study on the yield loss and economic threshold of alfalfa damaged by thrip, Odentothrips loti. Plant Prot. 2005;31:47–49.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

