Functions of Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes in Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle: A Review of Studies with Receptor-Knockout Mice
- PMID: 33477687
- PMCID: PMC7831928
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020926
Functions of Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes in Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle: A Review of Studies with Receptor-Knockout Mice
Abstract
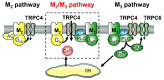
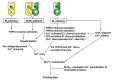
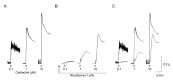
Parasympathetic signalling via muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) regulates gastrointestinal smooth muscle function. In most instances, the mAChR population in smooth muscle consists mainly of M2 and M3 subtypes in a roughly 80% to 20% mixture. Stimulation of these mAChRs triggers a complex array of biochemical and electrical events in the cell via associated G proteins, leading to smooth muscle contraction and facilitating gastrointestinal motility. Major signalling events induced by mAChRs include adenylyl cyclase inhibition, phosphoinositide hydrolysis, intracellular Ca2+ mobilisation, myofilament Ca2+ sensitisation, generation of non-selective cationic and chloride currents, K+ current modulation, inhibition or potentiation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ currents and membrane depolarisation. A lack of ligands with a high degree of receptor subtype selectivity and the frequent contribution of multiple receptor subtypes to responses in the same cell type have hampered studies on the signal transduction mechanisms and functions of individual mAChR subtypes. Therefore, novel strategies such as genetic manipulation are required to elucidate both the contributions of specific AChR subtypes to smooth muscle function and the underlying molecular mechanisms. In this article, we review recent studies on muscarinic function in gastrointestinal smooth muscle using mAChR subtype-knockout mice.
Keywords: gastrointestinal tract; knockout mouse; muscarinic receptor subtypes; non-selective cationic channels; signal transduction pathways; smooth muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Caulfield M., Birdsall N. International Union of Pharmacology. XVII. Classification of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998;50:279–290. - PubMed
-
- Jositsch G., Papadakis T., Haberberger R., Wolff M., Wess J., Kummer W. Suitability of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antibodies for immunohistochemistry evaluated on tissue sections of receptor gene-deficient mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2009;379:389–395. doi: 10.1007/s00210-008-0365-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

