Delivery of the 5-HT2A Receptor Agonist, DOI, Enhances Activity of the Sphincter Muscle during the Micturition Reflex in Rats after Spinal Cord Injury
- PMID: 33477834
- PMCID: PMC7832846
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10010068
Delivery of the 5-HT2A Receptor Agonist, DOI, Enhances Activity of the Sphincter Muscle during the Micturition Reflex in Rats after Spinal Cord Injury
Abstract
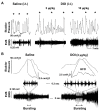
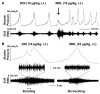
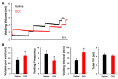
Traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) interrupts spinobulbospinal micturition reflex pathways and results in urinary dysfunction. Over time, an involuntary bladder reflex is established due to the reorganization of spinal circuitry. Previous studies show that manipulation of serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) receptors affects recovered bladder function, but it remains unclear if this receptor regulates the activity of the external urethral sphincter (EUS) following SCI. To elucidate how central and peripheral serotonergic machinery acts on the lower urinary tract (LUT) system, we employed bladder cystometry and EUS electromyography recordings combined with intravenous or intrathecal pharmacological interventions of 5-HT2A receptors in female SCI rats. Three to four weeks after a T10 spinal transection, systemic and central blockage of 5-HT2A receptors with MDL only slightly influenced the micturition reflex. However, delivery of the 5-HT2A receptor agonist, DOI, increased EUS tonic activity and elicited bursting during voiding. Additionally, subcutaneous administration of DOI verified the enhancement of continence and voiding capability during spontaneous micturition in metabolic cage assays. Although spinal 5HT2A receptors may not be actively involved in the recovered micturition reflex, stimulating this receptor subtype enhances EUS function and the synergistic activity between the detrusor and sphincter to improve the micturition reflex in rats with SCI.
Keywords: electromyogram; external urethral sphincter; micturition; serotonin; spinal cord injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

