Age by Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Interactions on Bronchodilator Response in Asthmatics
- PMID: 33477890
- PMCID: PMC7833432
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm11010059
Age by Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Interactions on Bronchodilator Response in Asthmatics
Abstract
An unaddressed and important issue is the role age plays in modulating response to short acting β2-agonists in individuals with asthma. The objective of this study was to identify whether age modifies genetic associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with bronchodilator response (BDR) to β2-agonists. Using three cohorts with a total of 892 subjects, we ran a genome wide interaction study (GWIS) for each cohort to examine SNP by age interactions with BDR. A fixed effect meta-analysis was used to combine the results. In order to determine if previously identified BDR SNPs had an age interaction, we also examined 16 polymorphisms in candidate genes from two published genome wide association studies (GWAS) of BDR. There were no significant SNP by age interactions on BDR using the genome wide significance level of 5 × 10-8. Using a suggestive significance level of 5 × 10-6, three interactions, including one for a SNP within PRAG1 (rs4840337), were significant and replicated at the significance level of 0.05. Considering candidate genes from two previous GWAS of BDR, three SNPs (rs10476900 (near ADRB2) [p-value = 0.009], rs10827492 (CREM) [p-value = 0.02], and rs72646209 (NCOA3) [p-value = 0.02]) had a marginally significant interaction with age on BDR (p < 0.05). Our results suggest age may be an important modifier of genetic associations for BDR in asthma.
Keywords: asthma; bronchodilator response; genome-wide interaction study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
Figures
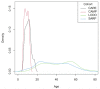
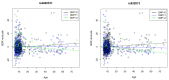

References
-
- The Global Asthma Report 2018. [(accessed on 11 September 2019)]; Available online: http://www.globalasthmareport.org/burden/burden.php.
-
- Palmer L.J., Celedón J.C., Chapman H.A., Speizer F.E., Weiss S.T., Silverman E.K. Genome-wide linkage analysis of bronchodilator responsiveness and post-bronchodilator spirometric phenotypes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003;12:1199–1210. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg125. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- U01HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141826/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139634/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL65899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL152244/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL146980/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL130629/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD085993/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- K01 HL125858/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL123915/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

