Extracellular Prolidase (PEPD) Induces Anabolic Processes through EGFR, β1-integrin, and IGF-1R Signaling Pathways in an Experimental Model of Wounded Fibroblasts
- PMID: 33477899
- PMCID: PMC7833428
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020942
Extracellular Prolidase (PEPD) Induces Anabolic Processes through EGFR, β1-integrin, and IGF-1R Signaling Pathways in an Experimental Model of Wounded Fibroblasts
Abstract
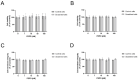
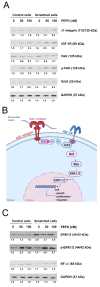
The role of prolidase (PEPD) as a ligand of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) was studied in an experimental model of wound healing in cultured fibroblasts. The cells were treated with PEPD (1-100 nM) and analysis of cell viability, proliferation, migration, collagen biosynthesis, PEPD activity, and the expressions of EGFR, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and β1-integrin receptor including downstream signaling proteins were performed. It has been found that PEPD stimulated proliferation and migration of fibroblasts via activation of the EGFR-downstream PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Simultaneously, PEPD stimulated the expression of β1-integrin and IGF-1 receptors and proteins downstream to these receptors such as FAK, Grb2, and ERK1/2. Collagen biosynthesis was increased in control and "wounded" fibroblasts under PEPD treatment. The data suggest that PEPD-induced EGFR signaling may serve as a new attempt to therapy wound healing.
Keywords: EGFR; IGF-1; PEPD; fibroblasts; prolidase; wound healing; β1-integrin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Palka J., Adelmann-Grill B.C., Francz P.I., Bayreuther K. Differentiation stage and cell cycle position determine the chemotactic response of fibroblasts. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 1996;34:121–127. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

