Dermatological Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- PMID: 33477990
- PMCID: PMC7835974
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10020364
Dermatological Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Abstract
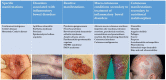
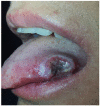
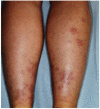
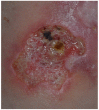
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) may be associated with extra-intestinal manifestations. Among these, mucocutaneous manifestations are relatively frequent, often difficult to diagnose and treat, and may complicate the course of the underlying disease. In the present review, a summary of the most relevant literature on the dermatologic manifestations occurring in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases has been reviewed. The following dermatological manifestations associated with IBDs have been identified: (i) specific manifestations with the same histological features of the underlying IBD (occurring only in Crohn's disease); (ii) cutaneous disorders associated with IBDs (such as aphthous stomatitis, erythema nodosum, psoriasis, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita); (iii) reactive mucocutaneous manifestations of IBDs (such as pyoderma gangrenosum, Sweet's syndrome, bowel-associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome, aseptic abscess ulcers, pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans, etc.); (iv) mucocutaneous conditions secondary to treatment (including injection site reactions, infusion reactions, paradoxical reactions, eczematous and psoriasis-like reactions, cutaneous infections, and cutaneous malignancies); (v) manifestations due to nutritional malabsorption (such as stomatitis, glossitis, angular cheilitis, pellagra, scurvy, purpura, acrodermatitis enteropathica, phrynoderma, seborrheic-type dermatitis, hair and nail abnormalities). An accurate dermatological examination is essential in all IBD patients, especially in candidates to biologic therapies, in whom drug-induced cutaneous reactions may assume marked clinical relevance.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; dermatological manifestations; inflammatory bowel disease; skin; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


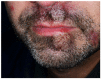
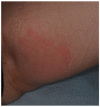


Comment in
-
A case of erythema nodosum concomitant with ulcerative colitis relieved by tofacitinib.Dermatol Ther. 2022 Dec;35(12):e15963. doi: 10.1111/dth.15963. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Dermatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36366826 No abstract available.
References
-
- Harbord M., Annese V., Vavricka S.R., Allez M., Acosta M.B.-D., Boberg K.M., Burisch J., De Vos M., De Vries A.-M., Dick A.D., et al. The First European Evidence-based Consensus on Extra-intestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis. 2016;10:239–254. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjv213. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

