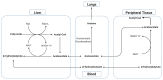
The Ketogenic Diet: Breath Acetone Sensing Technology
- PMID: 33478049
- PMCID: PMC7835940
- DOI: 10.3390/bios11010026
The Ketogenic Diet: Breath Acetone Sensing Technology
Abstract
The ketogenic diet, while originally thought to treat epilepsy in children, is now used for weight loss due to increasing evidence indicating that fat is burned more rapidly when there is a low carbohydrate intake. This low carbohydrate intake can lead to elevated ketone levels in the blood and breath. Breath and blood ketones can be measured to gauge the level of ketosis and allow for adjustment of the diet to meet the user's needs. Blood ketone levels have been historically used, but now breath acetone sensors are becoming more common due to less invasiveness and convenience. New technologies are being researched in the area of acetone sensors to capitalize on the rising popularity of the diet. Current breath acetone sensors come in the form of handheld breathalyzer devices. Technologies in development mostly consist of semiconductor metal oxides in different physio-chemical formations. These current devices and future technologies are investigated here with regard to utility and efficacy. Technologies currently in development do not have extensive testing of the selectivity of the sensors including the many compounds present in human breath. While some sensors have undergone human testing, the sample sizes are very small, and the testing was not extensive. Data regarding current devices is lacking and more research needs to be done to effectively evaluate current devices if they are to have a place as medical devices. Future technologies are very promising but are still in early development stages.
Keywords: acetone; breathalyzer; ketogenic diet; semi-conductor metal oxides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epilepsy and the ketogenic diet: assessment of ketosis in children using breath acetone.Pediatr Res. 2002 Sep;52(3):443-8. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200209000-00023. Pediatr Res. 2002. PMID: 12193682
-
Guiding Ketogenic Diet with Breath Acetone Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Oct 28;18(11):3655. doi: 10.3390/s18113655. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30373291 Free PMC article.
-
Breath acetone is a reliable indicator of ketosis in adults consuming ketogenic meals.Am J Clin Nutr. 2002 Jul;76(1):65-70. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/76.1.65. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002. PMID: 12081817
-
Assessing ketosis: approaches and pitfalls.Epilepsia. 2008 Nov;49 Suppl 8:20-2. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01826.x. Epilepsia. 2008. PMID: 19049579 Review.
-
Understanding the Potential of WO₃ Based Sensors for Breath Analysis.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Oct 29;16(11):1815. doi: 10.3390/s16111815. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27801881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Invasive Breath Analysis for Disease Screening and Diagnoses.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Apr 12;12(4):235. doi: 10.3390/bios12040235. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448295 Free PMC article.
-
Innovations and applications of ketone body monitoring in diabetes care.Diabetol Int. 2024 May 28;15(3):370-378. doi: 10.1007/s13340-024-00735-4. eCollection 2024 Jul. Diabetol Int. 2024. PMID: 39101172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Microsphere-Based Sensor for Point-of-Care and Non-Invasive Acetone Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jul 3;15(7):429. doi: 10.3390/bios15070429. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40710079 Free PMC article.
-
A humidity-resistant and room temperature carbon soot@ZIF-67 composite sensor for acetone vapour detection.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Feb 16;5(7):1956-1969. doi: 10.1039/d3na00050h. eCollection 2023 Mar 28. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 36998651 Free PMC article.
-
Nanowire Array Breath Acetone Sensor for Diabetes Monitoring.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 May;11(19):e2309481. doi: 10.1002/advs.202309481. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38477429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marie L.D.A. La Lutte Contrjz L’épilepsie Par La Rééducation Alimentaire. Epilepsia. 1911;A2:265–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1911.tb03003.x. - DOI
-
- Wilder R. The effects of ketonemia on the course of epilepsy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1921;2:307–308.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources