Bridging the Gap between Vertebrate Cytogenetics and Genomics with Single-Chromosome Sequencing (ChromSeq)
- PMID: 33478118
- PMCID: PMC7835784
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12010124
Bridging the Gap between Vertebrate Cytogenetics and Genomics with Single-Chromosome Sequencing (ChromSeq)
Abstract
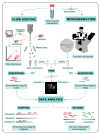
The study of vertebrate genome evolution is currently facing a revolution, brought about by next generation sequencing technologies that allow researchers to produce nearly complete and error-free genome assemblies. Novel approaches however do not always provide a direct link with information on vertebrate genome evolution gained from cytogenetic approaches. It is useful to preserve and link cytogenetic data with novel genomic discoveries. Sequencing of DNA from single isolated chromosomes (ChromSeq) is an elegant approach to determine the chromosome content and assign genome assemblies to chromosomes, thus bridging the gap between cytogenetics and genomics. The aim of this paper is to describe how ChromSeq can support the study of vertebrate genome evolution and how it can help link cytogenetic and genomic data. We show key examples of ChromSeq application in the refinement of vertebrate genome assemblies and in the study of vertebrate chromosome and karyotype evolution. We also provide a general overview of the approach and a concrete example of genome refinement using this method in the species Anolis carolinensis.
Keywords: Anolis; DOPseq; chromosomics; cytogenomics; de novo assembly; flow sorting; karyotype; microdissection; reference genomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chromosomics: Bridging the Gap between Genomes and Chromosomes.Genes (Basel). 2019 Aug 20;10(8):627. doi: 10.3390/genes10080627. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31434289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-generation sequencing of vertebrate experimental organisms.Mamm Genome. 2009 Jun;20(6):327-38. doi: 10.1007/s00335-009-9187-4. Epub 2009 May 19. Mamm Genome. 2009. PMID: 19452216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vertebrate Chromosome Evolution.Annu Rev Anim Biosci. 2021 Feb 16;9:1-27. doi: 10.1146/annurev-animal-020518-114924. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Annu Rev Anim Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33186504 Review.
-
CSA: A high-throughput chromosome-scale assembly pipeline for vertebrate genomes.Gigascience. 2020 May 1;9(5):giaa034. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giaa034. Gigascience. 2020. PMID: 32449778 Free PMC article.
-
Towards complete and error-free genome assemblies of all vertebrate species.Nature. 2021 Apr;592(7856):737-746. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03451-0. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33911273 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Integration of fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromosome-length genome assemblies revealed synteny map for guinea pig, naked mole-rat, and human.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 29;13(1):21055. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46595-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38030702 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosomal Evolution of the Talpinae.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 19;14(7):1472. doi: 10.3390/genes14071472. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510376 Free PMC article.
-
Shining Light in Mechanobiology: Optical Tweezers, Scissors, and Beyond.ACS Photonics. 2024 Mar 11;11(3):917-940. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.4c00064. eCollection 2024 Mar 20. ACS Photonics. 2024. PMID: 38523746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of Astyanax mexicanus (Characiformes, Characidae) chromosome 1 structure reveals unmapped sequences and suggests conserved evolution.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 18;19(11):e0313896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313896. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39556552 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-Centric View of Genome Organization and Evolution.Genes (Basel). 2021 Aug 12;12(8):1237. doi: 10.3390/genes12081237. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Editorial A reference standard for genome biology. [(accessed on 6 December 2018)];Nat. Biotechnol. 2018 36:1121. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4318. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nbt.4318. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Braasch I., Gehrke A.R., Smith J.J., Kawasaki K., Manousaki T., Pasquier J., Amores A., Desvignes T., Batzel P., Catchen J., et al. The spotted gar genome illuminates vertebrate evolution and facilitates human-teleost comparisons. Nat. Genet. 2016;48:427–437. doi: 10.1038/ng.3526. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

