Financial burden impact quality of life among lymphatic Filariasis patients
- PMID: 33478462
- PMCID: PMC7818560
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-021-10170-8
Financial burden impact quality of life among lymphatic Filariasis patients
Abstract
Background: Human lymphatic filarial pathology is the leading cause of disability and poverty among people living with the infection. The second goal of the Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (GPELF) is to manage the disease's morbidity to improve patients' quality of life. Consequently, the current study assessed the overall quality of life of lymphatic filariasis (LF) pathology patients in some selected endemic communities in rural Ghana.
Method: In the present study, the Lymphatic Filariasis Quality of Life Questionnaire (LFSQQ) was used to evaluate the effect of lymphatic filariasis on the quality of life of people, with the disease in nine (9) communities in the Ahanta West District of the Western Region of Ghana where mass drug administration is being implemented for the past twenty years. Pearson's correlation, linear regression, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) analyses were used to assess the associations between the LFSQQ instrument domains.
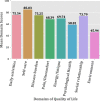
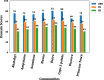
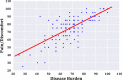
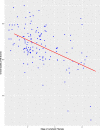
Results: Of the 155 study participants recruited, 115 (74.19%) were females, and 40 (25.81%) males. A greater proportion of the study participants (40, 25.8%) were presented with stage two (2) lymphoedema, while only two patients had stage seven (7) lymphoedema. The average of the overall quality of life scores of study participants was 68.24. There was a negative Pearson correlation (r = - 0.504, p-value < 0.001) between the stage of lymphoedema (severity of the disease) and the quality of life of the LF patients. In addition, a clear pattern of positive correlation (r = 0.71, p-value < 0.001) was observed between the disease burden and pain/discomfort domains of the study participants. Whereas the highest domain-specific score (85.03) was observed in the domain of self-care, we noted that the environmental domain, which consists of the financial status, was the lowest (45.94) among the study participants.
Conclusion: Our findings support previous works on the reduced quality of life among lymphatic filariasis patients with pathology. In this study, our results reveal a depressing financial condition among people presenting with late stages of LF pathologies, which eventually reduces their well-being.
Keywords: Ghana; Lymphatic Filariasis; Quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hemalatha K, V, R. P . Impact of Lymphatic Filariasis on Quality of Life of Affected Individuals : A Community Based Cross Sectional Survey. 2016. pp. 13–18.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Lymphatic filariasis : progress of disability Filariose lymphatique : compte rendu des activités de prévention des incapacités. 2004.
-
- Gyapongl J. Descriptive epidemiology of lymphatic filariasis in Ghana. 1996. pp. 26–30. - PubMed
-
- Programme TG, Filariasis EL, Programme L. Weekly epidemiological record Relevé épidémiologique hebdomadaire. 2018. pp. 589–604.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

