Neonicotinoids disrupt memory, circadian behaviour and sleep
- PMID: 33479461
- PMCID: PMC7820356
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-81548-2
Neonicotinoids disrupt memory, circadian behaviour and sleep
Abstract
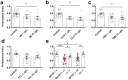
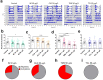
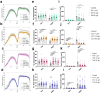
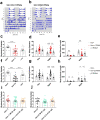
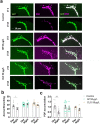
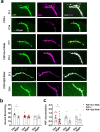
Globally, neonicotinoids are the most used insecticides, despite their well-documented sub-lethal effects on beneficial insects. Neonicotinoids are nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists. Memory, circadian rhythmicity and sleep are essential for efficient foraging and pollination and require nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signalling. The effect of field-relevant concentrations of the European Union-banned neonicotinoids: imidacloprid, clothianidin, thiamethoxam and thiacloprid were tested on Drosophila memory, circadian rhythms and sleep. Field-relevant concentrations of imidacloprid, clothianidin and thiamethoxam disrupted learning, behavioural rhythmicity and sleep whilst thiacloprid exposure only affected sleep. Exposure to imidacloprid and clothianidin prevented the day/night remodelling and accumulation of pigment dispersing factor (PDF) neuropeptide in the dorsal terminals of clock neurons. Knockdown of the neonicotinoid susceptible Dα1 and Dβ2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits in the mushroom bodies or clock neurons recapitulated the neonicotinoid like deficits in memory or sleep/circadian behaviour respectively. Disruption of learning, circadian rhythmicity and sleep are likely to have far-reaching detrimental effects on beneficial insects in the field.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neonicotinoids disrupt circadian rhythms and sleep in honey bees.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 21;10(1):17929. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72041-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33087835 Free PMC article.
-
Neonicotinoid insecticides differently modulate acetycholine-induced currents on mammalian α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;175(11):1987-1998. doi: 10.1111/bph.14018. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28853147 Free PMC article.
-
Mode of Action of Neonicotinoid Insecticides Imidacloprid and Thiacloprid to the Cockroach Pameα7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 13;22(18):9880. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189880. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576043 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview on the Effect of Neonicotinoid Insecticides on Mammalian Cholinergic Functions through the Activation of Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 6;17(9):3222. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17093222. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32384754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selected neonicotinoids and associated risk for aquatic organisms.Vet Med (Praha). 2023 Aug 31;68(8):313-336. doi: 10.17221/78/2023-VETMED. eCollection 2023 Aug. Vet Med (Praha). 2023. PMID: 37982123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Avian migration clocks in a changing world.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2024 Jul;210(4):691-716. doi: 10.1007/s00359-023-01688-w. Epub 2024 Feb 2. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38305877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unravelling nicotinic receptor and ligand features underlying neonicotinoid knockdown actions on the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles gambiae.Open Biol. 2024 Jul;14(7):240057. doi: 10.1098/rsob.240057. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Open Biol. 2024. PMID: 39043224 Free PMC article.
-
Using radio frequency identification and locomotor activity monitoring to assess sleep, locomotor, and foraging rhythmicity in bumblebees.STAR Protoc. 2021 Jun 11;2(2):100598. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100598. eCollection 2021 Jun 18. STAR Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34169292 Free PMC article.
-
On-Site Detection of Neonicotinoid Pesticides Using Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles and Halogen Bonding.ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2023 Apr 24;6(10):8367-8381. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c00618. eCollection 2023 May 26. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2023. PMID: 37260915 Free PMC article.
-
BioClocks UK: driving robust cycles of discovery to impact.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025 Jan 23;380(1918):20230345. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0345. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39842476 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gallai N, Salles J-M, Settele J, Vaissière BE. Economic valuation of the vulnerability of world agriculture confronted with pollinator decline. Ecol. Econ. 2009;68:810–821. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.06.014. - DOI
-
- Hallmann CA, Sorg M, Jongejans E, Siepel H, Hofland N, Schwan H, Stenmans W, Müller A, Sumser H, Hörren T, Goulson D, de Kroon H. More than 75 percent decline over 27 years in total flying insect biomass in protected areas. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0185809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185809. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

