Network meta-analysis of biologic treatments for psoriasis using absolute Psoriasis Area and Severity Index values ≤1, 2, 3 or 5 derived from a statistical conversion method
- PMID: 33480102
- PMCID: PMC8248394
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.17130
Network meta-analysis of biologic treatments for psoriasis using absolute Psoriasis Area and Severity Index values ≤1, 2, 3 or 5 derived from a statistical conversion method
Abstract
Background: In practice, the goal of treatment for patients with psoriasis is to achieve almost clear or clear skin and maintain disease control, regardless of baseline disease severity. However, identifying absolute Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) values for new treatment goals is challenging, as most clinical trials report relative PASI 50, 75, 90 or 100 improvements but rarely absolute PASI values achieved.
Objective: Our objective was to illustrate a statistical conversion method that was developed to derive absolute PASI values from available clinical trial data on relative PASI improvements. The results of network meta-analyses (NMAs) based on these derived data were then compared with those of NMAs based on the corresponding relative PASI improvement data for selected biologics for moderate-to-severe psoriasis.
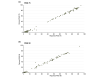
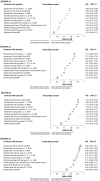
Methods: The PASI statistical conversion method was applied to relative PASI improvement data for 11 biologic treatment regimens and placebo at 12 weeks using data from 50 published studies. The respective proportions of patients reaching absolute PASI values ≤1, 2, 3 or 5 were then calculated. Frequentist NMAs (Rücker method) were subsequently used to compare efficacy results across relative and absolute PASI data.
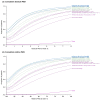
Results: The ranking of included treatment regimens for patients achieving absolute PASI 0 to 8 was aligned with results for relative PASI scores (from 100 to 60) at end of induction therapy. Across the range of PASI scores considered, the most effective treatment regimens based on both absolute and relative PASI NMAs were brodalumab 210 mg every 2 weeks and ixekizumab 80 mg every 2 weeks, followed by guselkumab 100 mg every 8 weeks and risankizumab 150 mg every 12 weeks.
Conclusion: Data generated using this mathematical model will be useful to inform ongoing scientific discussions on treatment goals in the absence of primary absolute PASI data for all available treatments for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Figures

References
-
- Puig L. PASI90 response: the new standard in therapeutic efficacy for psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2015; 29: 645–648. - PubMed
-
- Nast A, Smith C, Spuls PI et al. EuroGuiDerm Guideline for the systematic treatment of psoriasis vulgaris; 2020. URL https://www.edf.one/dam/jcr:c80dd166‐c66f‐4548‐a7ed‐754f5e2687d0/Living_... (last accessed: 04 November 2020).
-
- Cline A, Hill D, Lewallen R, Feldman SR. Current status and future prospects for biologic treatments of psoriasis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016; 12: 1273–1287. - PubMed
-
- Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Papp KA et al. Phase 3 trials of ixekizumab in moderate‐to‐severe plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375: 345–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

